This is Chapter Three of seven. In this chapter, our ancestors really expand their horizons. They discover what it was like to be an exile in nearby Holland, and also, what it was like to boldly venture much further — to the unknown place in the New World across a great ocean.
In the century before our ancestors sailed on the Mayflower, there was much debate going on within the religious circles of Europe, about individual authority for direct religious experience. It is difficult for many of us today to quite understood how radical these thinkers were. This period was known as the Protestant Reformation and its development helped lead our ancestors (both figuratively and literally) out of the Old World and into a New World.
Martin Luther and the 95 Theses
“The Protestant Reformation was a religious reform movement that swept through Europe in the 1500s. It resulted in the creation of a branch of Christianity called Protestantism, a name used collectively to refer to the many religious groups that separated from the Roman Catholic Church due to differences in doctrine.

(Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons).
The Protestant Reformation began in Wittenberg, Germany, on October 31, 1517, when Martin Luther, a teacher and a monk, published a document he called [the] ‘Disputation on the Power of Indulgences, or 95 Theses’. The document was a series of 95 ideas about Christianity that he invited people to debate with him. These ideas were controversial because they directly contradicted the Catholic Church’s teachings.” (National Geographic)
The Spread of Calvinism —
“Written between 1536 and 1539, [John] Calvin’s ‘Institutes of the Christian Religion’ was one of the most influential works of the era. Toward the middle of the 16th century, these beliefs were formed into one consistent creed which would shape the future definition of the Reformed faith. Through Calvin’s missionary work in France, his program of reform eventually reached the French-speaking provinces of the Netherlands.
Reformed theologians believe that God communicates knowledge of himself to people through the Word of God. People are not able to know anything about God except through this self-revelation. (With the exception of general revelation of God; ‘His invisible attributes, His eternal power and divine nature, have been clearly seen, being understood through what has been made, so that they are without excuse’ [Romans 1:20].) Speculation about anything which God has not revealed through his Word is not warranted.” (Wikipedia)

Portrait of John Calvin, by Artist unknown. Title page to Christianae religionis institutio,
by John Calvin, circa 1536. (See footnotes).
The Political Background —
“The Pilgrim migration can be viewed as an aspect of the major changes in church and state throughout Europe which we know as the Renaissance and Reformation and the beginnings of colonialism. The urge to return to an ideal form of the Christian church in conformity with what is described in the New Testament arose from a critical reading of ancient texts which characterized other fields of scholarly enquiry at the time as well. Similar study of the Bible had inspired Martin Luther, Menno Simons,and John Calvin. The state Church of England rejected by the Pilgrims was, however, part of a much larger movement opposed to the religious dominance of Rome and the political dominance of the Catholic Hapsburg Empire.” (Leiden American Pilgrim Museum – LAPM)
The English King “Henry VIII created the Church of England as a religious body unique from the Roman Catholic Church in order to achieve his goal of divorcing his first wife, Catherine of Aragon, in an attempt to remarry and father sons to continue his dynasty. The primary difference between the Catholic Church and the Church of England is that the Catholic Church recognizes the Pope as the Head of the Church, while the Church of England is led by the English monarch as Supreme Head of the Church.” (See footnotes). (1)
James I and England
In 1603, Queen Elizabeth of England was succeeded by James VI and I (James Stuart). He was the King of Scotland, the King of England and the King of Ireland, who faced many complicated religious challenges during his reigns in Scotland and England. For the purposes of this narrative, we are referring to him as James I and focusing solely on England.

(Image courtesy of the Collection Museum Prinsenhof Delft / Loan Mauritshuis, The Hague).
“James I disliked Robert Browne’s followers, who did not care for the episcopal hierarchy of the Anglican state church. The king maintained that God had bestowed upon him his position as absolute ruler, making any criticism of him sacrilege. On James’s orders, the ‘Brownists’, the separatist movement to which the Pilgrims belonged, were fined, imprisoned or banished.”
“On his succession to the English throne in 1603, James was impressed by the church system he found there, which still adhered to an episcopate [the Bishops of the Church of England] and supported the monarch’s position as the head of the church. On the other hand, there were many more Roman Catholics in England than in Scotland, and James inherited a set of penal laws which he was constantly exhorted to enforce against them. Before ascending to the English throne, James had [pledged] that he would not persecute “any that will be quiet and give but an outward obedience to the law,” but he soon reinforced strict penalties against Catholics. Partly triggered by Catholics’ disillusionment with the new King, the Gunpowder Plot of 1605 led to a new wave of anti-Catholicism and even harsher legislation.
James took an interest in the scholarly decisions of [religious] translators, [and] often participated in theological debate. A notable success was the commissioning of a new translation of the Bible, completed in 1611, which became known as the King James… and “Ironically, the most popular translation of that Bible, the King James version, came to be under a monarch who, in a sense, drove the Pilgrims from England.” (Wikipedia) and (National Endowment For The Humanities – NEFTH) (2)
It was one thing to disagree with the church hierarchy, but the political problem was that the head of the Church of England
Cited within the article,
was also the reigning king. And James I,
was a strong believer in unity when it came to his church;
he had no patience with religious rebels…
“Anyone who separates from the church is not just separating from the church, but they’re separating from royal authority,”
explains Michael Braddick, a historian at the University of Sheffield. “And that’s potentially very dangerous.”
Who Were the Pilgrims Who Celebrated the First Thanksgiving?
by Craig Lambert
HUMANITIES, November/December 2015, Volume 36, Number 6
Historic Labels — Identifying Who “The Others” Are
Many historic references cite different terms when referring to the Pilgrims. They were religious non-conformists, who referred to themselves as Saints, not as Pilgrims. Later in time, William Bradford, the Plymouth Colony Governor, once referred to the Saints as Pilgrims, (from an Old Testament reference) and the name eventually stuck. In addition, “The English term ‘pilgrim’ originally comes from the Latin word peregrinus (per, through + ager, field, country, land), which means a foreigner, a stranger, someone on a journey, or a temporary resident”. (University of York)
People who disagreed with their views referred to them as English Dissenters, or Separatists, or (incorrectly) as Puritans, which was initially a pejorative phrase . The Separatists held many of the same beliefs as the Puritans, but “believed that their congregations should separate from the state church, which led to their being labelled Separatists.” In contrast, although they were perceived as similar, the Puritans wanted to work from within the established church framework to purify it from within.
“Pilgrims and Puritans get blended into one big origin story,
Abram Van Engen,
when in fact they are different peoples
with different colonies, patents, and perspectives.”
A History of American Puritan Literature*
*The Puritans “came to the Americas a decade later, in greater numbers, and with far more institutional resources at their disposal. Whereas 102 Pilgrims came over on the Mayflower, 1,000 Puritans came to Boston. Unlike the Pilgrims, the Puritans had an official charter from the King of England to establish a colony and had not separated from the Church of England.” (Washington University)
Finally, Some older texts refer to them as the Brownists. “The Brownists were a Christian group in 16th-century England. They were a group of English Dissenters or early Separatists from the Church of England. They were named after Robert Browne, [of] the 1550s, [and] the terms were used to describe them by outsiders…” (Wikipedia) (3)

(Image courtesy of History.com)
A Radical Notion At The Time
Having a direct experience of God, without intermediaries, was essentially what the Pilgrims sought in their religious beliefs. As such, “The Pilgrims strongly believed that the Church of England, and the Catholic Church, had strayed beyond Christ’s teachings, and established religious rituals, and church hierarchies, that went against the teachings of the Bible. This belief put them at odds with church officials, who in the early years of King James I tried to have them arrested and thrown in jail for refusing to participate in church rituals.”
The Pilgrim church had a number of religious differences with orthodoxy. Here were some of the main points and differences as further explained by Caleb Johnson’s Mayflower History.com —
Predestination
The Pilgrims believed that before the foundation of the world, God predestined to make the world, man, and all things. He also predestined, at that time, who would be saved, and who would be damned.
Sacraments and Popery
To the Pilgrims, there were only two sacraments: baptism and the Lord’s Supper. The other sacraments of the Church of England and Roman Catholic church (Confession, Penance, Confirmation, Ordination, Marriage, Confession, Last Rites) were inventions of man, had no scriptural basis, and were therefore superstitions — even to the point of being heretical or idolatrous.
Church Hierarchy
The legitimacy of the Pope, the Saints, bishops, and the church hierarchy were rejected, as was the veneration of relics. The church of the Pilgrims was organized around five officers: pastor, teacher, elder, deacon, and deaconess (sometimes called the “church widow”). However, none of the five offices was considered essential to the church.
Infant Baptism
The Pilgrims believed baptism was the sacrament that wiped away Original Sin, and was a covenant with Christ and his chosen people, and therefore children should be baptized as infants.
Holy Days and Religious Holidays
The Pilgrims faithfully observed the Sabbath, and did not work on Sunday. Even when the Pilgrims were exploring Cape Cod, they stopped everything and stayed in camp on Sunday to keep the Sabbath. The Pilgrims did not celebrate Christmas and Easter.

(Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons via The Library of Congress).
Religious Texts
The Pilgrims used the Geneva edition of the Bible, first published in English in 1560. The translation and footnotes of the Geneva Bible were made by early Calvinists more trustworthy to the Pilgrims than the later King James Bible (first published in 1611) whose translation and footnotes were written by the Anglican church hierarchy.”
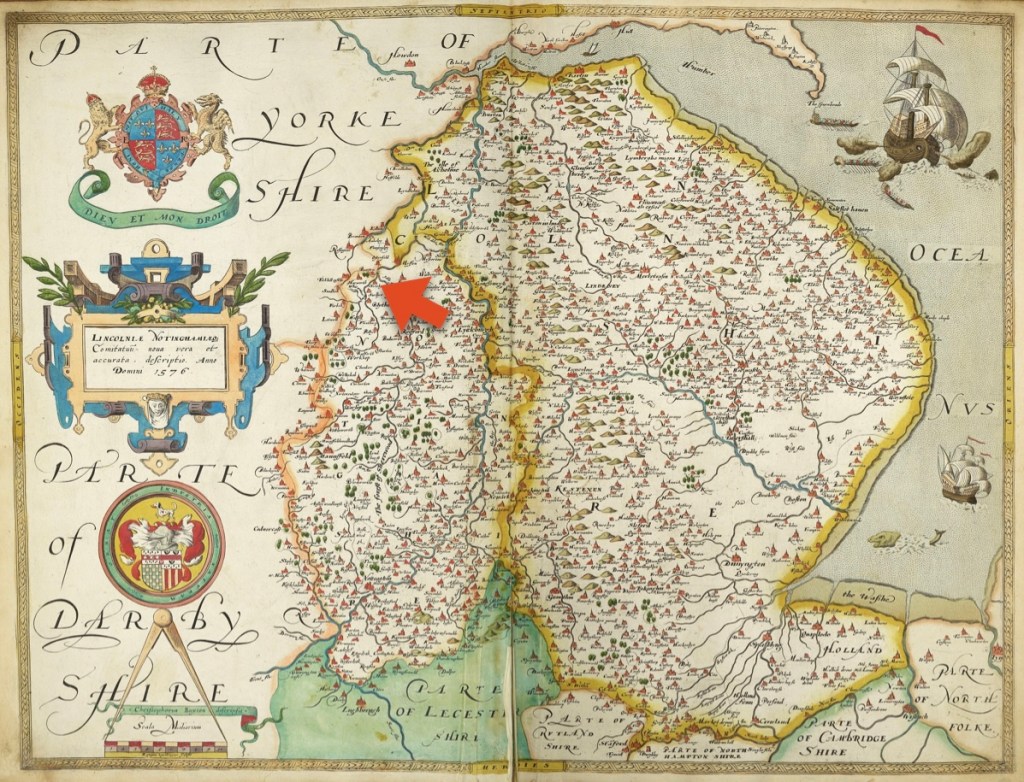
“Although most Puritans wanted to reform or ‘purify’ the Church of England [from within], a number of groups believed that the Church was irreparable. One such group of Separatists, as they were known, had its roots in the small village of Scrooby, in Nottinghamshire, England. It was in Scrooby, in the year 1607, that a group of people came together to form an illegal separate church after withdrawing from their Anglican parishes. As English citizens were required by law to become members of the Church of England, many of the Scrooby group suffered persecution, in the form of fines and imprisonments.” (See footnotes, The Plymouth Colony Archive Project – TPCAP) (4)
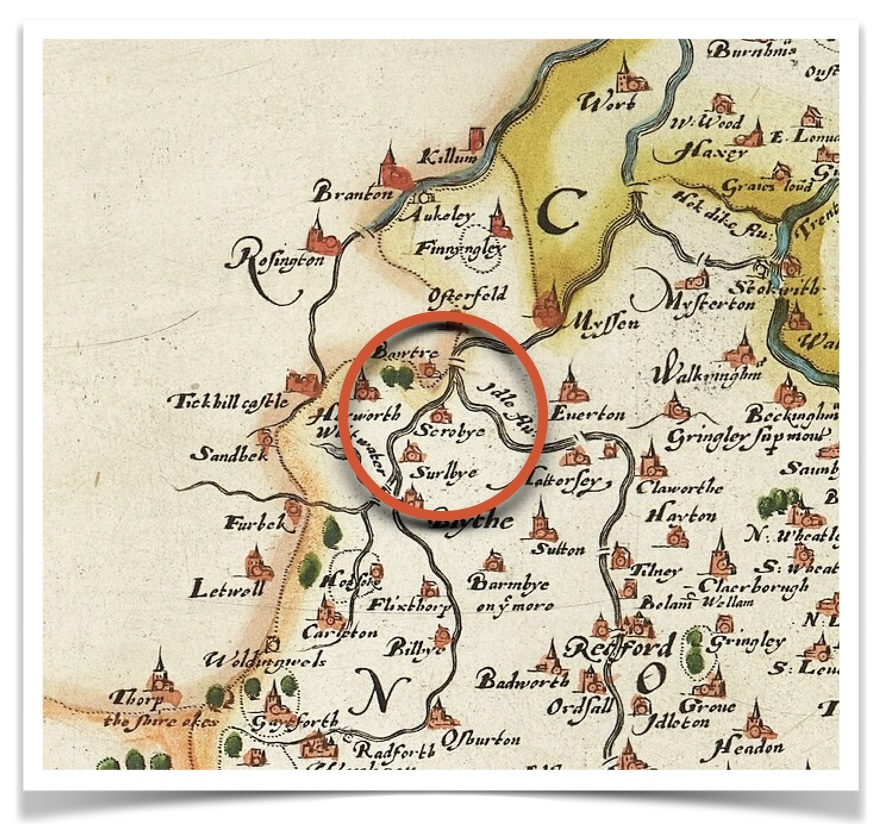
William Brewster and the Scrooby Village Congregation
William Brewster is an important figure in the life of our ancestor George Soule. Likely born in 1566 or 1567, probably in Scrooby, Nottinghamshire — he was an educated English official. He was an illustrious figure in the Plymouth community, and became the senior elder and the leader there, by virtue of his education and existing stature with those immigrating from the Netherlands.
“Beginning in 1580, he studied briefly at Cambridge University, before entering the service of William Davison, ambassador to the Netherlands, in 1584, giving him opportunity to hear and see more of reformed religion. [As such] Brewster was the only Pilgrim with political and diplomatic experience. With his mentor Davison in prison*, Brewster had returned home to Scrooby for a time, where he took up his father’s former position as postmaster in 1590.”
Sidebar: Davison was an English diplomat and secretary to Queen Elizabeth I. As a Secretary of some influence, he was active in forging alliances with England’s Protestant friends in Holland and Scotland to prevent war with France. He was involved in the 1587 execution of Mary, Queen of Scots, and was made a scapegoat for this event.

Using the manor house at Scrooby was a very brave move for this group of people. At that time, property like this was technically owned by the King, even though the era of manor houses was giving way to one of private country mansions. “The Tudor period (16th century) of stability in England saw the building of the first of the unfortified great houses. During the second half of the reign of Queen Elizabeth I and under her successor King James I, the first mansions designed by architects began to make their appearance [and came to] epitomize the English country house.”
“Following the campaign led by Archbishop Bancroft to force puritan ministers out of the Church of England, the Brewsters joined the Brownist church led by John Robinson and Richard Clifton, inviting them to meet in their manor house in Scrooby. Restrictions and pressures applied by the authorities convinced the congregation of a need to emigrate to the more sympathetic atmosphere of Holland, and Brewster organized the removal. Leaving England without permission was illegal at the time, so that departure was a complex matter. On its first attempt, in 1607, the group was arrested at Scotia Creek, but in 1608, Brewster and others were successful in leaving from the Humber,” [on the east coast of northern England]. (Wikipedia) (5)
Fleeing to First to Amsterdam, and Then to Leyden, Holland
“Robinson’s church lived for a year in Amsterdam, but in 1609 one of their fellow Brownist churches there led by John Smyth became the first Baptist church. In the controversy that followed, Robinson and Brewster decided to take their church to Leiden.” (Wikipedia)

Leyden, or Leiden?
A comment about spelling — the spelling of the city name at the time when the Pilgrims resided there was Leyden (with a y). That is the spelling we prefer to use for this history. However in the present day, the name is spelled Leiden (with an i), which you will see in some quoted contexts.

“The move to Leiden was carefully prepared. The city’s permission included the statement, now famous, that Leiden ‘refuses no honest people free entry to come live in the city, as long as they behave honestly and obey all the laws and ordinances, and under those conditions the applicants’ arrival here would be pleasing and welcome.’ Putting inaction to fine words, the city refused to denounce the Pilgrims when the British ambassador requested information about them because they were rumored to be banished Brownists. Town officials let it be known that the city had heard nothing of their being either banished or Brownists, but rather that they were honest people of the Reformed religion – and would His Excellency please excuse them to the King in this matter.” (See footnotes, Leiden American Pilgrim Museum – LAPM) (6)

when they lived there. (Image courtesy of Wikiart.org).
The Brewster Press
The city of Leyden was the second largest in the Netherlands, with around 40,000 people living there by 1620. “Leiden’s city walls had to expand in 1611, when no more houses could be built in the gardens of the older residences. A city extension was carried out all along the northern side of the town. About a third of Leiden’s inhabitants were refugees from Belgium, and among so many thousands of newcomers, the group of 100 Pilgrims arriving in 1609 attracted little attention.”

(Image courtesy of Doopsgezinden en Remonstranten Leiden. See footnotes).
“Brewster lived near St Peter’s church (Dutch: Pieterskerk) in Leiden with his wife and children. He was chosen as assistant and later as an elder to Pastor John Robinson. (He was still an elder when he travelled to Plymouth Colony in 1620).
In Leiden, the group managed to make a living. Brewster had struggled for money in Amsterdam, but in Leiden he taught English to [Calvinist] university students. Leiden was a fountain of academic publishing; and it was again becoming a major artistic center as it had been in the earlier 16th century. When the Pilgrims were in Leiden, the Latin School counted among its pupils Rembrandt van Rijn.” (LAPM)

Perth Assembly, 1619
(Image courtesy of David Calderwood, Leiden University Libraries).
“A year before their departure for America, the Pilgrims published this pamphlet in Leiden. It was immediately banned in England since it criticised royal decisions that had been made during an assembly in Perth, Scotland in 1618. In this pamphlet, the Pilgrims express their dislike of the celebration of Christmas and Easter, the episcopal hierarchy and the practice of kneeling during Holy Communion.”
“Brewster printed and published religious books for sale in England, but they were prohibited there. The press was prolific, printing “seven books against the regime of the Church of England in 1618 alone. In 1618, Brewster’s press published ‘De regimine Ecclesianae Scoticanae’ by Scottish minister David Calderwood, which was highly critical of James I and his government. They followed it up in April 1619 with ‘Perth Assembly.’
King James ordered an international manhunt for the writer and printer, but Brewster went underground. According to historian Stephen Tomkins, Brewster handed himself over to the Dutch authorities, who refused to send him to his death in England and so told James that they had arrested the wrong person and let him go. Tomkins judges that Brewster’s printing operation ‘came close to ruining his church’s plans for America.’ ” (Wikipedia) Clearly, King James I was against minority opinion being shared publicly.
For our ancestor George Soule, most of his future life experiences would be shaped by this period with William Brewster, and his life underground. (See The Soule Line, A Narrative — One). (7)

(Copperstitch according to Adrian van Venne), from: J. Cats “Old age, country life, and court thoughts, on Sorgh-Vliet” Amsterdam, 1656. (Image courtesy of the Leiden American Pilgrim Museum).
Pilgrim Occupations in Leyden
With so many refugees living in Leyden, the city welcomed some of them to work at the looms. Leiden American Pilgrim Museum notes, that among the Pilgrims, some worked at other professions —
- Jonathan Brewster was a merchant who produced ribbon, that he exported to England.
- Samuel Fuller, the Pilgrims’ physician in Plymouth Colony, was a serge-weaver in Leiden.
- Myles Standish, the colony’s future military leader, was a soldier.
- Isaac Allerton, later to become well-known as a merchant and Plymouth Colony’s representative in England, was a tailor in Leiden, a trade he had learned in London.
- Edward Winslow assisted William Brewster as a printer, (and significantly for us, had George Soule travel with him on the Mayflower as his Servant).
- Nicholas Claverley was one of Leiden’s first tobacco-pipe makers, involved with other Englishmen in the tobacco trade that could be found wherever English soldiers were garrisoned. (Note: Nicholas Claverley is recorded as being part of the Pilgrim group in Leyden, but he did not travel on the Mayflower).
“But adults and children alike, who’d been farmers in England, now toiled from dawn to dusk, six or seven days a week, weaving cloth in the textile factories. Even with such hardships, the Pilgrims later regarded their Leiden years as a type of glory days, whose difficulties were nothing compared with the ordeals they faced in America.” (NEFTH) (8)

Clockwise from the top: Street views of Beschuitsteeg (Biscuit) Alley), a portrait of Pilgrim Edward Winslow over the fireplace mantle, a view of the storage pantry, the sleeping area*, the museum exterior at the intersection of Beschuitsteeg 9 and Nieuwstraat. *Note: Curiously, in that era, people did not sleep lying down, but instead, slept in a sitting position. Two people and a nursing child would have slept in this nook).
Choosing to Travel to The British Colonies in North America
By 1617, the Separatists were getting anxious to move again. “Their biggest concern after a decade in this foreign land was that their children were becoming Dutch,’ Nathaniel Philbrick, the author of Mayflower explains. ‘They were still very proud of their English heritage. They were also fearful that the Spanish were about to attack again.’
Indeed, a conflict was building between Spain’s Catholic King and European Protestant powers, which would soon embroil the continent in the Thirty Years’ War. Radical Protestants viewed this as a battle between the forces of good (Protestantism) and evil (Roman Catholicism), little short of Armageddon. ‘Everything seemed to be on the edge of complete meltdown,’ Philbrick says. ‘And so they decided it’s time to pull the ripcord once again. Even if it meant leaving everything they had known all their lives.’ ” (NEFTH)
However by then, something had changed, as something had started to shift in their demeanor by living in Leyden, and this affected their views in the future Plymouth Colony —
“They were much more tolerant than people think, particularly for their time,” [Historian Jeremy Bangs] says. ‘They did not require people in the Plymouth Colony to follow Calvinist beliefs. This led to a conscious construction of a society with separation of church and state.’ Bangs, whose extensive research has made him one of the pre-eminent authorities on the Pilgrims, cites a 1645 proposal by the Plymouth Colony leaders that Jews, Catholics, Unitarians and many other sects be accepted in the Plymouth Colony.”
Further, in a Smithsonian magazine interview about her book, The World of Plymouth Plantation, historian Carla Pestana explores Plymouth’s grip on the American historical imagination. She says, “I do think that in Plymouth they tended to be somewhat more tolerant of alternate religious views. Decades later when the Harvard president openly explains that he’s a Baptist and has to leave Massachusetts, he goes to Plymouth. The first Quaker in Massachusetts who gets converted goes to Plymouth. I actually think that’s one reason why Plymouth wins in the sweepstakes for becoming the most important founding moment in the region. They don’t kill witches like Salem. They don’t kill Quakers like Boston. Some of the worst things that people in the late 18th century were starting to be embarrassed about, about their ancestors, didn’t happen in Plymouth.” (Smithsonian, for both Bangs, and Pestana)
We will be writing more about this evolution of their worldviews in the chapter, The Pilgrims — The Native Peoples.

by Adam Willaerts, circa 1620. When they left Leyden,“They boarded [canal boats] at the Rapenburg, not far from the Pieterskerk and John Robinson’s house.” (Vita Brevis) From there, they sailed to Delfshaven where the Speedwell was waiting to take them to England.
(Image courtesy of The Museum of Fine Arts Boston).
“Brewster and Robinson were the prime movers in the decision to sail for America, but once he was in hiding, the Separatists looked to their deacon John Carver and to Robert Cushman to carry on negotiations with the appropriate officials in London. Brewster returned to the Leiden congregation in 1620, when it was time for the Speedwell to sail to England. He had been hiding out in Netherlands and perhaps even England for the last year. At the time of his return, Brewster was the highest-ranking layman of the congregation and was their designated elder in Plymouth Colony.
When the passengers of the Mayflower landed at Plymouth Colony, Brewster became the senior elder, and so served as the religious leader of the colony in the colony, he became a Separatist leader and preacher, and eventually as an adviser to Governor William Bradford.
As the only university-educated member of the colony, Brewster took the part of the colony’s religious leader until pastor Ralph Smith arrived in 1629. Thereafter, he continued to preach irregularly until his death in April 1644. ‘He was tenderhearted and compassionate of such as were in misery,’ Bradford wrote, ‘but especially of such as had been of good estate and rank and fallen unto want and poverty.’ In 1632, he received lands in nearby Duxbury and removed from Plymouth to create a farm there.”
Our ancestor George Soule, had also done the same. (9)
Following are the footnotes for the Primary Source Materials,
Notes, and Observations
Martin Luther and the 95 Theses
(1) — nine records
National Geographic
The Protestant Reformation
https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/protestant-reformation/
Note: For the text.
Luther Posting His 95 Theses
by Ferdinand Pauwels
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Luther95theses.jpg#file
Note: For the painting.
Reformed Christianity
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reformed_Christianity
Note: For the text about John Calvin and The Spread of Calvinism.
Nationalmuseum (Stockholm, Sweden)
Martin Luther (portrait)
by Lucas Cranach the Elder, circa 1527
File:Martin Luther (1483-1546) (Lucas Cranach d.ä.) – Nationalmuseum – 22066.tif
https://collection.nationalmuseum.se/sv/collection/item/22066/
Note: For his portrait.
The Huntington Library
Globalizing the Protestant Reformations
[Title page of the]
Disputatio pro declaration virtutis indulgentiarum
(Disputation on the Power of Indulgences)
by Martin Luther, circa 1519
https://huntington.org/verso/globalizing-protestant-reformations
Note: For the book image.
Encyclopædia Britannica
John Calvin (portrait)
by Artist unknown
https://www.britannica.com/biography/John-Calvin#/media/1/90247/113479
Note: For his portrait.
[Title page of the]
Christianae religionis institutio
by John Calvin, circa 1536
File:Christianae religionis institutio (1536).jpg
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Christianae_religionis_institutio_(1536).jpg
Note: For the book image.
(LAPM)
Leiden American Pilgrim Museum
The Political Background
https://leidenamericanpilgrimmuseum.org/en/page/pilgrim-life-in-leiden-the-political-background
Note: For the text.
The Church of England & Henry VIII | Reformation & Events
https://study.com/academy/lesson/henry-viii-and-the-anglican-church.html#:~:text=Henry%20VIII%20created%20the%20Church,sons%20to%20continue%20his%20dynasty.
Note: For the text from Who created the Church of England and why? and What’s the difference between [the] Catholic [Church] and [the] Church of England?
James I and England
(2) — three records
James VI and I and Religious Issues
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/James_VI_and_I_and_religious_issues
Note: For the text.
Collection Museum Prinsenhof Delft / Loan Mauritshuis, The Hague
Portrait of Jacobus I, 1566-1625, (James I)
by Artist unknown
https://www.lakenhal.nl/en/story/images-and-credit-lines-pilgrims
Notes: For his portrait.
“James I disliked Robert Browne’s followers, who did not care for the episcopal hierarchy of the Anglican state church. The king maintained that God had bestowed upon him his position as absolute ruler, making any criticism of him sacrilege. On James’s orders, the ‘Brownists’, the separatist movement to which the Pilgrims belonged, were fined, imprisoned or banished.”
(NEFTH)
The National Endowment For The Humanities
Who Were the Pilgrims Who Celebrated the First Thanksgiving?https://www.neh.gov/humanities/2015/novemberdecember/feature/who-were-the-pilgrims-who-celebrated-the-first-thanksgiving
Notes: For the pull-quote and the text.
Historic Labels — Identifying Who “The Others” Are
(3) — six records
The University of York
Pilgrims and Pilgrimage
The Origins of the Terms ‘Pilgrim’ and ‘Pilgrimage’
https://www.york.ac.uk/projects/pilgrimage/intro.html#:~:text=The%20English%20term%20’pilgrim’%20originally,journey%2C%20or%20a%20temporary%20resident.
Note: For the text that is the Latin definition for Pilgrims.
English Dissenters
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/English_Dissenters
Note: For the text that defines English Dissenters.
Pilgrims (Plymouth Colony)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pilgrims_(Plymouth_Colony)
Note: For the text that defines Separatists.
Washington University Art & Sciences
Pilgrims, Puritans, and the importance of the unexceptional
by John Moore
https://artsci.washu.edu/ampersand/pilgrims-puritans-and-importance-unexceptional
Note: For the text that clarifies the differences between Pilgrims and Puritans, and for the pull-quote by Abram Van Engen.
Brownists
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brownists
Note: For the text that defines Brownists.
1600s Pilgrim Couple Kneeling In Prayer
painting by Herbert Paus, via History.com
The Puritans
https://www.history.com/topics/colonial-america/puritanism
Note: For the illustration of 1600s Pilgrim Couple Kneeling In Prayer.
A Radical Notion At The Time
(4) — four records
Caleb Johnson’s MayflowerHistory.com
Church and Religion
http://mayflowerhistory.com/religion
Note: For the text regarding key beliefs of the Pilgrim congregation.
File:Geneva Bible.jpg
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geneva_Bible.jpg
Note: For the image of the Geneva edition of the Bible, first published in English in 1560.
File:Lincolnia nottinghamia Atlas.jpg
by Christopher Saxton, 1576
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lincolnia_nottinghamia_Atlas.jpg
Note: For the map of Nottinghamshire and Lincolnshire from 1576. Atlas created by cartographer Christopher Saxton as part of his ‘Atlas of the Counties of England and Wales’. Contains hand-written marginal notes.
(TPCAP)
The Plymouth Colony Archive Project
by J. Jason Boroughs
http://www.histarch.illinois.edu/plymouth/jbthesis.html
Note: For the text from the section, Background: The colonization of New England.
William Brewster and the Scrooby Village Congregation
(5) — six records
William Brewster (Mayflower passenger)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Brewster_(Mayflower_passenger)
Note: For the text.
Scrooby
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scrooby
Note: For the text.
Scrooby Manor House (illustration)
by Artist unknown
https://christianheritage.info/places/united-kingdom/east-midlands/bassetlaw/site/scrooby-manor-house/
Note: For the illustration.
Daniel Crouch Rare Books
Saxton’s Seminal Atlas of England and Wales in full original colour, circa 1579
https://crouchrarebooks.com/product/atlas/saxtons-seminal-atlas-of-england-and-wales-in-full-original-colour/
Note: For the image of Queen Elizabeth I.
File:Lincolnia nottinghamia Atlas.jpg
by Christopher Saxton, 1576
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lincolnia_nottinghamia_Atlas.jpg
Note: For the map of Nottinghamshire and Lincolnshire from 1576. Atlas created by cartographer Christopher Saxton as part of his ‘Atlas of the Counties of England and Wales’. Contains hand-written marginal notes.
Manor House
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manor_house
Note: For text under the section, Decline of the Manor House.
Fleeing to First to Amsterdam, and Then to Leyden, Holland
(6) — six records
William Brewster (Mayflower passenger)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Brewster_(Mayflower_passenger)
Note: For the text.
Leiden Museum de Lakenhal
Permit from the city council of Leiden for 100 Englishmen
to be allowed to settle in Leiden, dated 12 February 1609.
Pilgrims to America — And The Limits of Freedom (Exhibition)
via Heritage Leiden, Stadsarchief 1574 – 1816
https://www.lakenhal.nl/en/story/images-and-credit-lines-pilgrims
Notes: (Left page only). This is the written agreement that granted permission for the Pilgrims – around 100 men and women – to settle in Leiden. The document was written on behalf of the city council by city secretary Jan van Hout on February 12, 1609. The religious community around John Robinson was probably larger than the hundred people mentioned in the agreement because children weren’t included.
(LAPM)
Leiden American Pilgrim Museum
Pilgrim Life in Leiden — Coming to Leiden
https://leidenamericanpilgrimmuseum.org/en/page/pilgrim-life-in-leiden-coming-to-leiden
Note 1: For the text.
Note 2: Borrowed image, Boats like these sailed from Amsterdam to Leiden. Engraving by Adrian van de Venne, ca. 1630
Family Search Blog
The Life and Legacy of William Brewster
https://www.familysearch.org/en/blog/william-brewster-legacy
Note: For his portrait.
Map of Holland: According to Astronomical Observations, Measurements of Schnellius & c. and the Superiorly Redesigned Special Maps of F. L. Güssefeld, circa 1791.
https://www.loc.gov/resource/gdcwdl.wdl_01132/?r=-0.547,0.047,2.094,1.047,0
Note 1: This map of the Netherlands coast is the work of Prussian cartographer Franz Ludwig Güssefeld (1744-1807). It was drawn based on the calculations of the renowned Dutch mathematician Willebrord Snellius (1580-1626), a professor of mathematics at the University of Leiden, who conceived the idea of measuring the earth using triangulation. Snellius’s discoveries helped to determine the radius of the earth as well as led to more accurate ways of measuring the distance between two cities.
Note 2: Adapted to document travel from Amsterdam to Leyden.
Winter Scene on a Canal
by Hendrick Avercamp, circa 1615
https://www.wikiart.org/en/hendrick-avercamp/winter-scene-on-a-canal
Note 1: For this painting.
Note 2: Avercamp was famed for both his winter landscape paintings and for his superior ability as a draftsman. Today, his drawings are highly valued and are considered to be accurate records of Dutch clothing and lifestyles from this time period.
The Brewster Press
(7) — four records
(LAPM)
Leiden American Pilgrim Museum
Pilgrim Life in Leiden — Leiden, a Fair and Beautiful City
https://leidenamericanpilgrimmuseum.org/en/page/pilgrim-life-in-leiden-leiden-a-fair-and-beautiful-city
Note: For the text.
Doopsgezinden en Remonstranten Leiden, > Geschiedenis
Map of Leiden
by Pieter Bast, circa 1600
https://doreleiden.nl/geschiedenis/
Note 1: For the map.
Note 2: The website section generally translates from the Dutch language as Church History of the Mennonites and Remonstrants
William Brewster (Mayflower passenger)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Brewster_(Mayflower_passenger)
Note: For the text.
(LAPM)
Leiden Museum de Lakenhal
Pilgrims to America — And The Limits of Freedom (Exhibition)
via Heritage Leiden, Stadsarchief 1574 – 1816
Perth Assembly, 1619
(Image courtesy of David Calderwood, Leiden University Libraries).
https://www.lakenhal.nl/en/story/images-and-credit-lines-pilgrims
Notes: “A year before their departure for America, the Pilgrims published this pamphlet in Leiden. It was immediately banned in England since it criticised royal decisions that had been made during an assembly in Perth, Scotland in 1618. In this pamphlet, the Pilgrims express their dislike of the celebration of Christmas and Easter, the episcopal hierarchy and the practice of kneeling during Holy Communion.”
Pilgrim Occupations in Leyden
(8) — three records
(LAPM)
Leiden American Pilgrim Museum
The life of man compared to a weaver’s shuttle.
(Copperstitch according to Adrian van Venne), from:
J. Cats “Old age, country life, and court thoughts, on Sorgh-Vliet”
Amsterdam, 1656 (For the title in English).
https://www.abebooks.de/servlet/BookDetailsPL?bi=31525694547&cm_sp=collections-_-2gwY4IoWG3dukN4eR0KkQ0_item_1_37-_-bdp
Note: The original image was obtained form from the Leiden American Pilgrim Museum in November 2023.
(LAPM)
Leiden American Pilgrim Museum
Pilgrim Life in Leiden — Pilgrim Occupations in Leiden
https://leidenamericanpilgrimmuseum.org/en/page/pilgrim-life-in-leiden-pilgrim-occupations-in-leiden
Note: For the text.
(NEFTH)
The National Endowment For The Humanities
Who Were the Pilgrims Who Celebrated the First Thanksgiving?https://www.neh.gov/humanities/2015/novemberdecember/feature/who-were-the-pilgrims-who-celebrated-the-first-thanksgiving
Note: For the text.
Choosing to Travel to The British Colonies in North America
(9) — five records
(NEFTH)
The National Endowment For The Humanities
Who Were the Pilgrims Who Celebrated the First Thanksgiving?https://www.neh.gov/humanities/2015/novemberdecember/feature/who-were-the-pilgrims-who-celebrated-the-first-thanksgiving
Note: For the text.
Smithsonian Magazine
The Pilgrims Before Plymouth
by John Hanc
https://www.smithsonianmag.com/travel/the-pilgrims-before-plymouth-111851259/
Note: For the text about religious tolerance.
Smithsonian Magazine
Why the Myths of Plymouth Dominate the American Imagination
by Karin Wulf
https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/why-myths-plymouth-dominate-american-imagination-180976396/
Note: For the text.
The Museum of Fine Arts Boston
The Departure of the Pilgrim Fathers from Delfshaven on Their Way to America on July 22, 1620.
by Adam Willaerts, circa 1620
https://www.mfa.org/article/2022/the-departure-of-the-pilgrim-fathers-from-delfshaven-on-their-way-to-america
Note: For the (possibly contemporanious to 1620) painting.
William Brewster (Mayflower passenger)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Brewster_(Mayflower_passenger)
Note: For the text.
