This is Chapter Two of eleven. In this chapter we introduce you to our 11x Great Grandfather David Du Four, who was the progenitor of our DeVoe line in North America. He had an interesting life in New Amsterdam, which in today’s world we know as one of the world’s most famous places — Manhattan, New York City.
“What’s in a name? That which we call a rose / By any other name would smell as sweet.” — William Shakespeare

Writer Chris Waugh comments that “William Shakespeare made these lines immortal in his legendary tale of star-crossed lovers named Romeo & Juliet. The question within the quote (What’s in a name?) is still regularly used today as a popular adage expressing the point that the name or label we put on things or persons may vary, but these can still accurately describe the subject at hand. Simply put: “It is what it is” and “You are what you are.”
In this part of our history, we’ve carefully observed that the DeVoe family surname varies much in spelling within the records. Do not be alarmed, because the spelling of family surnames in this pre-literate era was not yet considered to be very important. Among the jumble of variations you will observe here are: de Foar, De Foo, De Four, Du Four, De Vaux, Devauxe, De Voor, DeVors, Devoor, and DeVoe.

by James Riker, which is cited much in this history.
James Riker wrote in The Revised History of Harlem — “From Mons, the rich capital of this province, seated to the north of Avesnes… came David du Four… whose posterity, which became numerous in his coimtry [territory or country], changed the form of their name to Devoor and Devoe.”
Our research turned up a similar story of surname confusion with a French immigrant family named Vorce. Their history relates, “there is the same confusion as other family names arising from the fact of their being written by those unfamiliar with their correct spelling… [hence, converted] comfortably to the pronunciation of their Dutch neighbors.” They even quoted Riker’s speculative story about David Du Four, “…settled in Harlem, where… in 1662… he was residing when Nicholas de Vaux arrived from France. The surnames of each being so much alike, they may have been led to the conclusion they were kinsmen, which led DeFour to alter the F to V, which later became DeVors, Devoe and other forms of the name…” The Vorce family solved the confusion around their surname by deciding “they were all Dutch together.” It’s likely Du Four also decided: Let’s All Be Dutch. (1)
Was David Du Four Belgian?
Not really… Belgium didn’t exist then.
Belgium didn’t become Belgium until more than 200 years after David Du Four was born. From Wikipedia, “For most of its history, what is now Belgium was either a part of a larger territory, such as the Carolingian Empire, or divided into a number of smaller states, prominent among them being the Duchy of Brabant, the County of Flanders, the Prince-Bishopric of Liège, the County of Namur, the County of Hainaut [where he lived], and the County of Luxembourg. Due to its strategic location as a country of contact between different cultures, Belgium has been called the ‘crossroads of Europe’; for the many armies fighting on its soil, it has also been called the ‘battlefield of Europe’…”

(Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons).
Historically, there were royal families ruling Europe at this time, and conquest whether for resources, or for religious reasons, was in its heyday. The locations where the Du Fours lived were border areas, and hence regions of conflict, with battles fought repeatedly. Over the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries, this area was repeatedly attacked and occupied by the Dutch, Spanish, French, and English forces. (At the beginning of the David Du Four’s life, Spain was supposedly in control of the area where David lived — the Southern Netherlands — but, neighboring France, and also Holland, wanted control).
Observation: Like a tide that kept washing in and out, it was a long era of endless hostilities…
Here is the short history version, continuing with Wikipedia: “The Eighty Years’ War (1568–1648) later led to the split between a northern Dutch Republic and the Southern Netherlands from which Belgium and Luxembourg developed. The area, long a Habsburg stronghold, briefly came under Bourbon control during the War of the Spanish Succession.“

“The French Revolutionary wars led to Belgium becoming part of France in 1795. After the defeat of the French in 1814, the Congress of Vienna created two new states, the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg… The Southern Netherlands rebelled during the 1830 Belgian Revolution, establishing the modern Belgian state…” (2)
David Du Four Identified as a Walloon
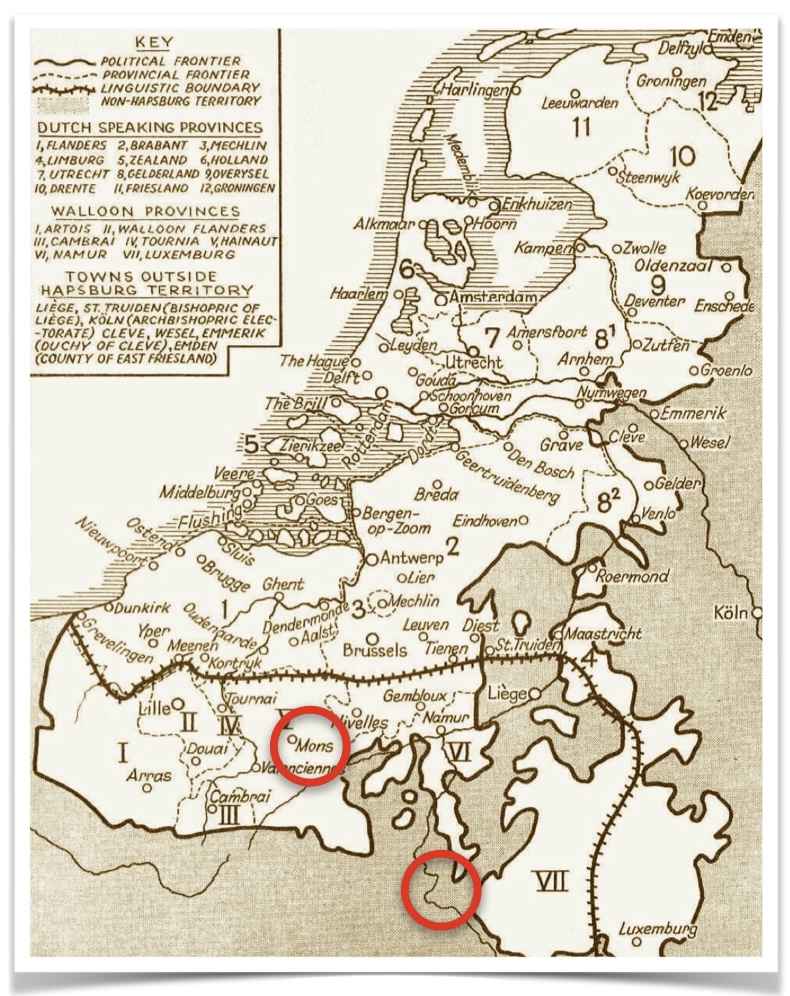
What this means essentially, is that he lived in a part of the world, where his cultural identity was not necessarily tied to the nearby borders (which were always in flux). The Wallonia region is part of the low-lying area of Flanders and the hilly region of the Ardennes. The ancestral description of being a Walloon refers to the ancient Roman populations of the Burgundian Netherlands. As we have learned, this area was occupied by other nations many times, consequently, the Walloons are a mixed cultural ancestry of French / Dutch / Germanic / Celtic. Today, being Walloon is still a unique culture-based identity, recognized within the present borders of Belgium. David likely spoke in French dialects (or perhaps some Flemish), and then later in life, in Dutch.
Wikipedia writes: “Walloons are primarily Roman Catholic, with a historical minority of Protestantism which dates back to the Reformation era.” We know through research in the historical records, that David Du Four was a Protestant, and that eventually his family were members of the Dutch Reformed Church. It also seems that they likely also had affinities with the Huguenots and their diaspora. We speculate that perhaps with all of the religious and political turmoil within Wallonia — this may have inspired him to relocate his family to New Amsterdam. (3)

The Man From Mons
David Du Four was born about 1620 at Bergen, Graafschap Henegouwen, Habsburgse Nederlanden (now Mons), Province de Hainaut, Southern Netherlands (now Belgium). He married twice — died before May 1699 at age 79, in Harlem or Turtle Bay, Manhattan, New York City, British American Colonies. [Note: New Amsterdam officially became New York City in the British American Colonies in 1665.]
Riker continues, “David Du Four, a native of Mons, in Hainault, upon this place being threatened by the successes of the French in the Walloon districts, retired [relocated] with others of his family to Sedan, and afterward to Amsterdam, where Du Four, though fitted by education for a better position, became an “opperman,” or drayman*. Left by the death of his wife, Marie Boulen [Boulyn], with a young child, Jean [John], born during their stay at Sedan…”
*A drayman was historically the driver of a dray, a low, flat-bed wagon without sides, pulled generally by horses or mules that were used to transport all kinds of goods. (Wikipedia)
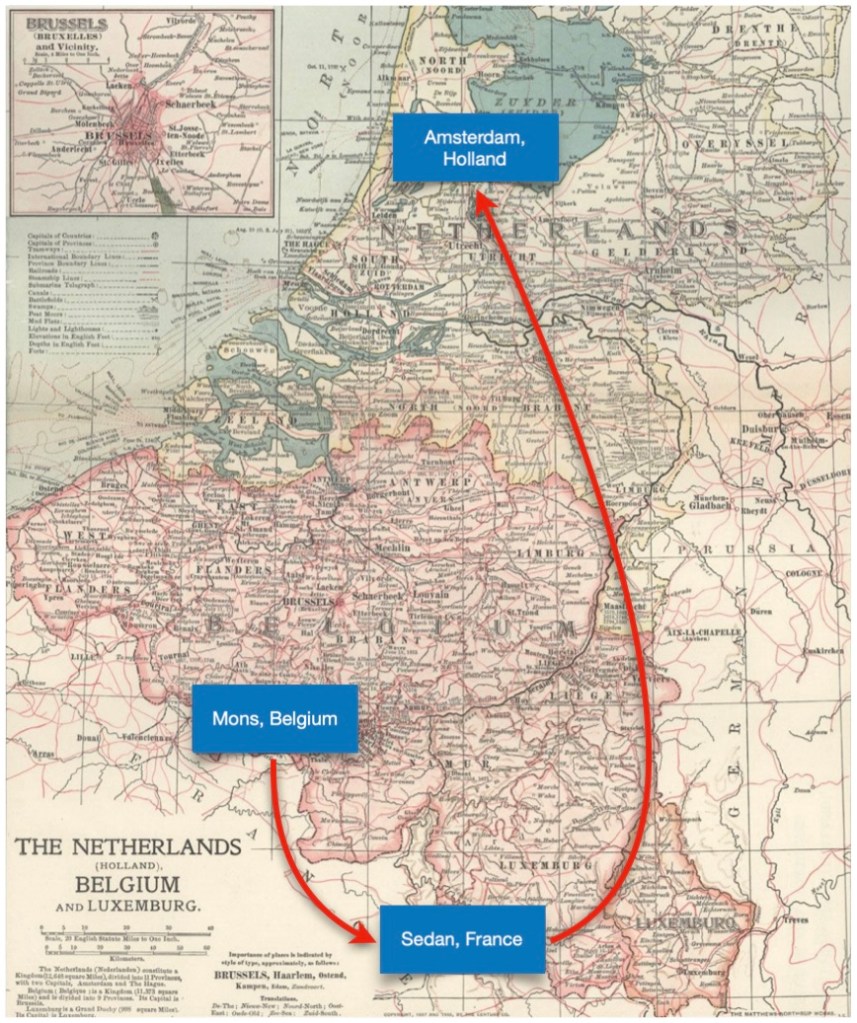
So, David’s first wife was Marie Boulyn. After they had relocated to Sedan, Ardennes, France, they had a boy whose name is John. Marie died sometime before 1657, and unfortunately, other than those facts, we really don’t know very much about her life.

In those days, especially if a man had a young child, he usually remarried pretty quickly. Again, from Riker: “…He found another companion in Jeanne Franzes, a lady of mature thirty-two years, from Queivrain, a little east of Mons, to whom he was married July 10th, 1657. That same year, with his new wife and his little son aforesaid [Jean], he sailed for Manhattan Island.”
Jeanne (Franzes) Du Four was born about 1625 at Quievremont, Province de Hainaut, Belgium — died after 1699 at Coale Kill, Turtle Bay, Manhattan, New Amsterdam, [New York City] after 74 years of age. Together, including the first born son John (1), they had seven children:
- John DeVoor (1), born about 1651, Sedan, Provence du Picardie, France — died before April 1724, Bloemendaal (Bloomingdale), Manhattan, New York City, British American Colonies, 73 years of age. (We are descended from John (1), whose name is also sometimes recorded as Jan, or Jean).
- Joris DeVoor, baptized July 7, 1658, and died before 1671
- David DeVoor, baptized October 5, 1659, and married Elizabeth (Jansen) DeVoor
- Pieter DeVoor, baptized October 15, 1662
- Anthony /Teunis DeVoor, born about 1664 — died August 31, 1668.
- Adriaen DeVoor, baptized January 28, 1665 — died before 1671
- Glaude DeVoor, born about 1667 — died after February 1687. (4)

A New Life In Harlem, New Amsterdam
We have not located the actual ship that David Du Four traveled on with his wife Jeanne and their son John. In fact, we are not sure if he arrived in 1657, or soon after, but we do know that he was there early on. We would be very lucky indeed if we found a ship manifest which names him, but at that time and in that era, it was not considered essential and was usually done only if the ship Captain thought it was necessary.
According to the Wikipedia article New Netherland, “The colony experienced dramatic growth during the 1650s, and became a major center for trade across the North Atlantic… The inhabitants of New Netherland were European colonists, Native Americans, and Africans imported as slave laborers. Not including Native Americans, the colonial population, many of whom were not of Dutch descent, was 4,301 in 1650, and 8,000 to 9,000 at the time of transfer to England in 1674.” (Colonial America to 1763)

Iconography of Manhattan Island, vol. IV plate 9, NYC Municipal Library.
We learned that he had been there “for three years” already by the “close of 1661” when it was documented in Riker’s Harlem history on page 183: “For three years this had been steadily growing, and at the close of 1661 contained over thirty adult male residents, mostly heads of families and freeholders. The following [top chart below] are the names of these pioneers, who first succeeded in planting the seeds of civilization and religion in this vicinity.” David is in the lower left column: note that he is listed by “nationality” as one of four Walloons, amongst French, Hollanders, Danes, Swedes, and Germans.
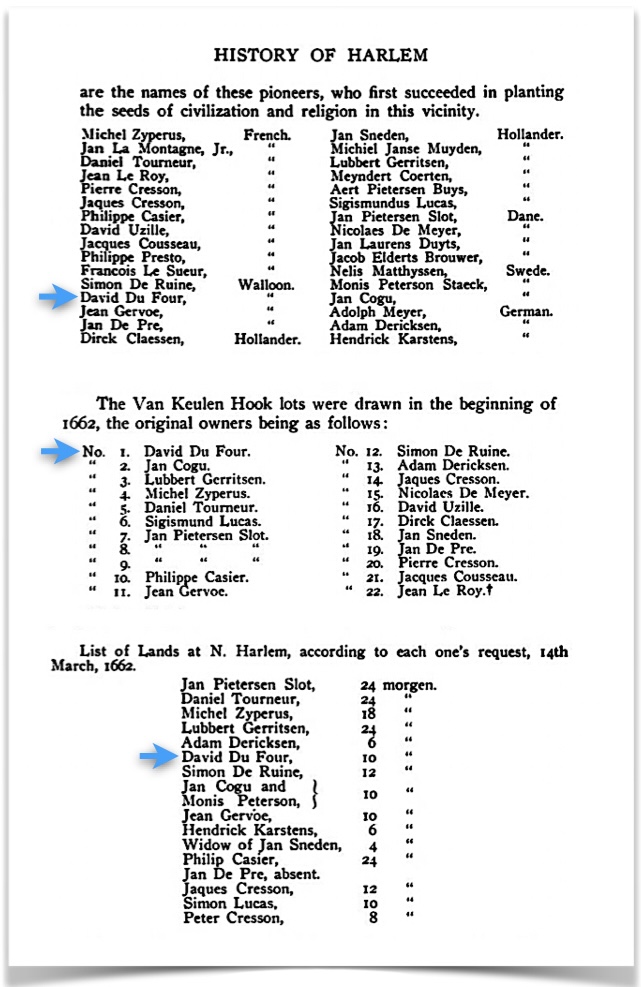
from pages 183, 186 and 190.
More records continued — The middle and bottom charts show that, not surprisingly, he was a farmer who owned land. From the Riker book, (paraphrasing)… It seems that he had tired of being a drayman, so then he was helping his neighbors by shepherding their cows and oxen. Things didn’t go so well and somehow he lost some of the oxen. His understandably upset neighbors complained loudly and he had to find something else to do.
Riker wrote “Du Four, the Amsterdam drayman, better at driving a team [farming] than stupid cows, was soon disgusted with his new occupation and turned it over to Jean Gervoe, the soldier. But now the cattle were not well looked after, as was alleged; in fact, some of the oxen, when needed for the yoke, were missing.” Apparently one of the ways that Du Four had to compensate his neighbors, was by paying them “guilders” and giving them butter…
In early 1662, “the Van Keulen Hook lots were drawn” and we noticed that David was first on the list. The final chart, from slightly later in 1662, shows the amount of land he owned: 10 morgen(s). Hopefully, his neighbors were no longer upset about the oxen incident.
The word morgen is from both the Dutch and German languages, and was used in their former colonies. It means morning. In practical usage it corresponds to as much land as one person can plow in a morning. As a unit of land measure it is equal to about two acres, or 0.8 hectare. (Dictionary.com) (5)
The Tragic Death of Young Teunis
On top of all the other many unfortunate things that our ancestors dealt with, one particular event has stood out in the historical record. The Du Four son Teunis (also known as Anthony), was accidentally murdered by John Copstaff, a drunken soldier who was shooting off a gun. He was only about four years old.(Riker) “In 1668, Du Four, passing in a canoe un the East River, and with him his child, Anthony, when, between Turtle Bay and Blackwell’s Island, John Copstaff, a drunken soldier in another boat, let off a gun which wounded little Anthony; this was on August 18, and he died August 31. Copstaff was convicted of manslaughter. Du Four being very ill, he and wife, Jannetie, made a will, September 14, 1671, naming…” The Will was a precaution against future unknown circumstances. Both of the Du Four parents lived for many more years. (6)
For. Every. Little. Kerfuffle. With. Your. Neighbors.
It seems that David Du Four had several showings in court because the records have survived. Here’s a little background on the times. In 1670s he was a “frequent flyer” at court, with several cases. In New Amsterdam, people from all walks of life could bring a case to court. They could defend the case themselves, or ask someone to speak for them. It was not necessary for them to have a lawyer for every case. This is because…

George Hayward for I.N. Stokes — Iconography of Manhattan Island.
(Image courtesy of the NYC Municipal Library).
(The following is extracted from Wikipedia)
“In the first years after Henry Hudson sailed up the river in 1609 and claimed the area for the Dutch East India Company and… there was no real New Netherlands government and judicial system. The inhabitants of the small trading community of Manhattan Island as well as the members of the crew of the ships that came to the area, were subject to the rule of their captains.”
Around 1621, “the Dutch presence in America intensified and… the New Amsterdam judicial system was initially developed privately by the Dutch East India Company, and gradually brought into closer conformity with Dutch law of the period. There were no jury trials and the use of arbitration to resolve disputes was widespread. Although the magistrates were laymen, they were generally held to have a good knowledge of Dutch (customary) law. The Dutch East India Company provided law books…”
To a degree, it seems like going to court was similar to being sent to the Principals Office. You had to go and plead your case. For example:
Case: Ariaen Vincent v. David de Four:
demand for payment of debt for a purchased horse: disputed: ordered to pay.

Our transcription will give you the gist of it:
Mr. Vincent (the plaintiff) demands payment from the defendant (Mr. de Four), the sum of 100 florins for a horse sold him last year, which defendant must pay him in beavers* at 20 florins the [a] piece. Defendant says, he did not make any agreement, how high the beavers should go [sounds like it was about the price per beaver?]. The W. Court condemns the defendant to satisfy and pay the plaintiff the sum demanded in beavers at 20 florins, unless he [the] defendant proves[s] the contrary at the next Court day. (7)

*We’re just guessing, but that must be about 5 beavers?
New Amsterdam Becomes New York
The English had their own designs for the developing colonies in the New World, and their plans did not include letting the Dutch keep control of Manhattan. However, getting the Dutch out of Manhattan is not the same as getting the Dutch out of Manhattan. Much culture remained, and it took years for things to settle out.
Wikipedia writes: “The city was captured by the English in 1664; they took complete control of the colony in 1674 and renamed it New York. [The official name change was in 1665]. However the Dutch landholdings remained, and the Hudson River Valley maintained a traditional Dutch character until the 1820s.” and “…British ships entered Gravesend Bay in modern Brooklyn, and troops marched to capture the ferry across the East River to the city, with minimal resistance: the governor at the time, Peter Stuyvesant, was unpopular with the residents of the city. Articles of Capitulation 1664 were drawn up, the Dutch West India Company’s colors were struck on September 8, 1664, and the soldiers of the garrison marched to the East River for the trip home to the Netherlands…”
By 1677, the residents of Harlem were collectively desiring to expand their land holdings under the British. This was something that involved the attentions of the new Governor Andros. James Riker writes, “No little concern was felt at the silence of Governor Andros in regard to his promise to distribute more land among them, and at reports of the large grants he was intending to make in their immediate vicinity, and even within their limits.” A resolution was reached and new farms were established along the banks of the East River. Later that year, “60 [acres were granted] to David du Four and son [likely John 1]” at Turtle Bay. (Notice that the land measurement units were no longer the Dutch morgens, but are now the English acres).

Side Bar Observation: My, how times change! To be honest, as descendants of David Du Four, we wish that our family still owned that land at Turtle Bay… Presently it is the site of the United Nations Headquarters in New York City.
“Standing on the eastern shore of Manhattan Island, on the banks of New York City’s East River, the 18-acre UN Headquarters remains both a symbol of peace and a beacon of hope.”

“During the latter half of 1946, following selection of the US as host country, a special UN site committee studied possible locations in such places as Philadelphia, Boston and San Francisco. While consideration was given at first to areas north of New York City, crowded Manhattan had not been seriously investigated. A last-minute offer of $8.5 million by John D. Rockefeller, Jr. for the purchase of the present site was accepted by a large majority of the General Assembly on 14 December 1946. The site chosen by the UN was a run-down area of slaughterhouses, light industry and a railroad barge landing.”
— History of United Nations Headquarters. (8)
Some Thoughts About Their Lives
Mary Louise Booth writes in her book, the History of The City of New York that, “In the beginning of the settlement, the people had been forced to accommodate themselves to the necessities of a new country, and their houses, furniture and apparel had necessarily been of the rudest kind… the houses were one story in height with two rooms on a floor. The chimneys were of wood, and the roofs were thatched with reeds and straw. The furniture was of the rudest kind, carpets were unknown, as indeed they continued to be for many years after; the stools and tables were hewn out of rough planks by the hands of the colonists; wooden platters and pewter spoons took the place of more expensive crockery, and naught but the indispensable chest of homespun linen and a stray piece of plate or porcelain, a treasured memento of the Fatherland, was seen to remind one of civilization.”

She continues, “As the forests became cleared away, and the colony increased, the style of living experienced a material change. The straw roofs and wooden chimneys were deemed unsafe, and were ordered to be removed ; and the settlers commenced to build their houses of brick and stone…

The windows were small and the doors large; the latter were divided horizontally, so that, the upper half being swung open, the burgher could lean on the lower and smoke his pipe in peaceful contemplation. Not less comfortable were the social “ stoeps,” and the low, projecting eaves, beneath which the friendly neighbors congregated at twilight to smoke their long pipes and discuss the price of beaver-skins. These institutions have come down to our own times, and are still known and appreciated in the suburbs of the city.”

David Du Four died before May 1699 at age 79, in Harlem or Turtle Bay, Manhattan, New Amsterdam, [New York City]. His wife Jeanne (Frances) Du Four, died after 1699 at the same location after 74 years of age.

On September 14, 1671, after the unexpected death of their son Teunis, they had written a Will. Historian James Riker indicates that, more than twenty five years later “His will was proved May 1, 1699. It names his children Jan [John 1], David, Pieter and Glaude.” The Will had not been updated in those years, and not all of these sons had survived as long as their father, or mother. (9)
Importantly for our family, we are descended from the oldest son, John (1). We will write about the history of his family in the next chapter.
Following are the footnotes for the Primary Source Materials,
Notes, and Observations
“What’s in a name? That which we call a rose / By any other name would smell as sweet.”
(1) — eight records
“What’s In A Name?”
by Chris Haugh
http://www.historysharkproductions.com/whats-in-a-name.html
The Cobbe Portrait of WillIam Shakespeare (1564-1616)
File:Cobbe portrait of Shakespeare.jpg
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Cobbe_portrait_of_Shakespeare.jpg

Genealogy of the De Veaux Family
Introducing the Numerous Forms of Spelling the Name by Various Branches
and Generations in the Past Eleven Hundred Years
by Thomas F. De Voe
https://archive.org/details/genealogyofdevea00devo/page/n3/mode/2up
Revised History of Harlem (City of New York): Its Origin and Early Annals
by James Riker
https://archive.org/details/revisedhistoryh00unkngoog/page/n12/mode/2up
Note: For general biographical information —
Book page: 65, Digital page: 64/907
Book page: 193, Digital page: 192/907
Book page: 408, Digital page: 408/907
VORCE
https://freepages.rootsweb.com/~hubbard/genealogy/NNY_index/vorce.html
and
Genealogical and Family History of Northern New York:
A Record of The Achievements of Her People in the Making of a Commonwealth and The Founding of a Nation
by William Richard Cutter, 1847 edition
https://archive.org/details/genealogicalfami02incutt/page/430/mode/2up
Book page: 431, Digital page: 430/860
Was David Du Four Belgian?
(2) — four records
Belgium’s Independence (1830 – present time)
“… A provisional government declared independence on October 4th, 1830.”
https://www.belgium.be/en/about_belgium/country/history/belgium_from_1830#:~:text=Following%20this%20rising%20Belgium%20separated,or%20who%20had%20special%20qualifications.
History of Belgium
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_Belgium
Map of the Netherlands in the Shape of a Lion, by Leo Belgicus, circa 1650
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Joannes_van_Deutecum_-_Leo_Belgicus_1650_-_published_by_Claes_Jansz_Visscher_Amsterdam.jpg
Note: For the map image.
Sanderus Antique Maps & Books
Northern Netherlands (VII Provinces), by Pieter Mortier. c. 1705
https://sanderusmaps.com/our-catalogue/antique-maps/europe/low-countries-netherlands/northern-netherlands-vii-provinces-by-pieter-mortier
“United Provinces of the Netherlands with their Acquisitions in Flanders, Brabant, Limburg, and Lyege and the Places which they possessed on the Rhine, in the Duchy of Cleves, and in the Archbishopric and Electorate of Cologne.”
Note: For the map image.
David Du Four Identified as a Walloon
(3) — three records
Namvrcvm Comitatvs, circa 1665 (map)
Prints Blaeu website
https://shop.blaeuprints.com/buy/maps/belgium/namur-malonne-jambes/?v=35357b9c8fe4
Note: ‘Namvrcvm Comitatvs’ translates to ‘County of Namur’ in English.

Walloons
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Walloons
and
Flag of Wallonia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flag_of_Wallonia
The Man From Mons
(4) — sixteen records
Map of Mons in the 16th Century, circa 1550
by Lodovico Guicciardini
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mons,_Belgium#/media/File:Stadsplan_Mons_uit_de_zestiende_eeuw.jpg
Note: For the map image.
Revised History of Harlem (City of New York): Its Origin and Early Annals
by James Riker
https://archive.org/details/revisedhistoryh00unkngoog/page/n12/mode/2up
Book pages: 99-100, Digital pages: 98-100/907
Note: For general biographical information.
Drayman
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drayman
Davidt de Four (abt. 1625 – bef. 1699)
https://www.wikitree.com/wiki/De_Four-2
Notes: Various points of information were pulled from this file:
– David Du Four’s exact birthplace
– The marriage certificate of David du Four and Jeanne Franzen —
https://archief.amsterdam/indexen/persons?ss=%7B%22q%22:%22Jeanne%20Fransen%22%7D
File number: OTR00052000157, Digital page: 15C/242, Left page, entry 1.
WikiTree
Marie (Boulen) Bouvie (1635 – bef. 1657)
https://www.wikitree.com/wiki/Boulen-1
Britannica.com
Map of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg, (c. 1900),
from the article Low Countries in the 10th edition of Encyclopedia Britannica
https://www.britannica.com/place/Low-Countries
Note: For the map image.
WikiTree
Jeanne Frans (abt. 1625 – aft. 1699)
https://www.wikitree.com/wiki/Frans-85
Note: For Jeanne (Franzen) Du Four’s death location
David Du Four
in the Netherlands, Select Marriages, 1565-1892
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/611949:60076?tid=&pid=&queryId=4ea6d503-225d-4d73-bf58-9ed334277e1c&_phsrc=LhJ2&_phstart=successSource
Early New Netherlands Settlers
David <?> Du Four, (Rn=25344)
https://freepages.rootsweb.com/~rclarke/genealogy/page1/dufour.htm
Jean Du Voor
in the U.S. and Canada, Passenger and Immigration Lists Index, 1500s-1900s
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/1620944:7486?ssrc=pt&tid=108788208&pid=162384998722
Notes: Sourced from the book The Early Germans of New Jersey, Their History, Churches and Genealogies, Dover, NJ: Theodore Frelinghuysen Chambers, 1895, located at: https://archive.org/details/earlygermansofne00cham/page/344/mode/2up?view=theater&q=%22Du+Voor%22
Book pages: 344-345, Digital pages: 334-345/667
Baptisms from 1639 to 1730 in the Reformed Dutch Church, New York
by Thomas Grier Evans
https://archive.org/details/baptismsfrom163921evan/page/n11/mode/2up
Notes: These are transcribed records. The following children of David du Four and Jeanne (Frans) Du Four are confirmed in this book, as follows:
Joris, Book page: 49, Digital page: 104/680
David, Book page: 54, Digital page: 114/680
Pieter, Book page: 67, Digital page: 126/680
Adriaen, Book page: 78, Digital page: 162/680
A New Life In Harlem, New Amsterdam
(5) — six records
New Netherland
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_Netherland
and
Colonial America to 1763
by Thomas L. Purvis.
https://archive.org/details/colonialamericat00purv_0/page/128/mode/2up
Book page: 128, Digital page: 128/386
New York City Department of Records & Information Services
View of New Amsterdam circa 1653,
copy of a 17th Century painting for I.N. Stokes —
Iconography of Manhattan Island, vol. IV plate 9, NYC Municipal Library.
From:
A Charter for New Amsterdam: February 2, 1653
https://www.archives.nyc/blog/2023/1/31/a-charter-for-new-amsterdam-february-2-1653
Revised History of Harlem (City of New York): Its Origin and Early Annals
by James Riker
https://archive.org/details/revisedhistoryh00unkngoog/page/n12/mode/2up
Note: For general biographical information, three charts,
and the oxen incident —
Book pages: 182-183, Digital page: 182/907
Book page: 186, Digital page: 186/907
Book page: 190, Digital page: 190/907
Book pages: 193-194, Digital pages: 192-194/907
Revised History of Harlem (City of New York): Its Origin and Early Annals
by James Riker
https://archive.org/details/revisedhistoryof01rike/page/n861/mode/2up?view=theater&q=1
Book page: Appendix F, pull-out map, Digital page: 862/952
Note: This is a different edition from the above reference, and is for the pull-out map Appendix F only featured at the back of this edition.
Dictionary.com
Morgen
https://www.dictionary.com/browse/morgen#
The Tragic Death of Young Teunis
(6) — one record
Revised History of Harlem (City of New York): its origin and early annals
by James Riker
https://archive.org/details/revisedhistoryh00unkngoog/page/n12/mode/2up
Book page: 408, Digital page: 408/907
Note: General biographical information.
For. Every. Little. Kerfuffle. With. Your. Neighbors.
(7) — six records
Stadt Huys (City Hall) in 1679
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:The_Stadt_Huys_(City_Hall)_of_New_York_in_1679_at_Pearl_Street.jpg
New Amsterdam Judicial System
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_Amsterdam_judicial_system
New York Municipal Archives
Guide to the records of New Amsterdam, 1647-1862
Collection No. MSS 0040
https://www.nyc.gov/assets/records/pdf/Dutch-NewAmsterdam_MSS0040_MASTER.pdf
The records of New Amsterdam from 1653 to 1674 anno Domini
Vol. VII. Court minutes of New Amsterdam
https://www.ancestry.com/imageviewer/collections/12896/images/dvm_PrimSrc000280-01255-0?treeid=&personid=&queryId=efac883e-ba59-4547-b7e9-bfda4edf6885&usePUB=true&_phsrc=LhJ1&_phstart=successSource&pId=2487&rcstate=dvm_PrimSrc000280-01255-0:1086,1979,1290,2028
Digital page: 2489/2765
New Amsterdam History Center
Mapping New York | Encyclopedia
Document: Minutes | Case | Philip Waldman v. Jan Smedes: default
https://encyclopedia.nahc-mapping.org/document/minutescasephilip-waldman-v-jan-smedes-default
New Amsterdam Becomes New York
(8) — seven records
Colonial History of the United States
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colonial_history_of_the_United_States
Conquest of New Netherland
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conquest_of_New_Netherland
Revised History of Harlem (City of New York): Its Origin and Early Annals
by James Riker
https://archive.org/details/revisedhistoryh00unkngoog/page/n12/mode/2up
Book page: 338-340, Digital page: 338-340/907
Note: General biographical information.
Map of New York City and of Manhattan Island with the American Defences in 1776.
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1878_Bien_and_Johnson_Map_of_New_York_City_(Manhattan_Island)_During_the_Revolutionary_War_-_Geographicus_-_NewYorkCity-johnsonbien-1878.jpg
Note: Used for two small inset maps to indicate where David Du Four owned property in Turtle Bay, Manhattan.
Turtle Bay, East River, N.Y. 1853
by George Hayward
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Turtle_Bay,_Manhattan_1853.jpg
Note: For the Turtle Bay image.
The Iconography of Manhattan Island, 1498-1909
by Isaac Newton Phelps Stokes,1867-1944; Victor Hugo Paltsits,1867-1952; Frederik Caspar Wieder, 1874-1943
https://archive.org/details/iconographyofman06stok/page/n239/mode/2up
Book page: 138, Digital page: 240/820.
Note: Left page, right column, under the heading: The Edmund Seaman Farm, Block Check List. 1345-1364-1325-1362, Introduction: The Grant to David du Four
History of United Nations Headquarters
https://www.un.org/sites/un2.un.org/files/headquarters.pdf
Note: For the building image.
Some Thoughts About Their Lives
(9) — six records

History of The City of New York, from its Earliest Settlement to The Present Time
by Booth, Mary Louise, 1831-1889
https://archive.org/details/historyofcityofn00boot_0/page/194/mode/2up
Dutch Cottage in New York, 1679
The New York Public Library Digital Collections
https://digitalcollections.nypl.org/items/510d47e1-2ba1-a3d9-e040-e00a18064a99
1648: A Glimpse into Dutch Household: Daily Life in New (Nieuw) Amsterdam
https://www.history101.nyc/dutch-household-new-amsterdam-1600s?v=2
David Du Four
in the New York County, New York, U.S., Wills and Probate Records, 1658-1880 (NYSA)
J0038-82: Probated Wills, 1671-1815 > Wills, Box 04-06, Crispell, Cornelius-Erwin, Samuel, 1767-1778
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/52776:60387?tid=&pid=&queryId=f8d0f93f-3723-4704-8f8a-6f507ee548b1&_phsrc=LiJ42&_phstart=successSource
Digital pages: 197-201/964
and
David Du Foor
in the New York, U.S., Wills and Probate Records, 1659-1999
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/1747140:8800?tid=&pid=&queryId=14cf0f49-97b0-412e-82e5-d6dab8e8581c&_phsrc=LhJ4&_phstart=successSource
Digital pages: 501-504/688

Calendar of Wills on File and Recorded in the Offices of the Clerk of the Court of Appeals, of the County Clerk at Albany, and of the Secretary of State, 1626-1836
by Fernow, Berthold, 1837-1908, Comptroller of the New York (State) Court of Appeals; Albany County (N.Y.); New York (State) Secretary’s Office
https://archive.org/details/calendarwillson00appegoog/page/97/mode/2up?view=theater
Book page: 97, Digital page: 97/657, Left page, entry 3