This is Chapter Six of seven. In this chapter, our ancestors who have been in New Hampshire since it was a Province and part of British North America, made the major decision to move Westward. They packed their belongings and left New Hampshire and headed to New York State.
(Image courtesy of Boston Rare Maps).
Be Fruitful and Multiply
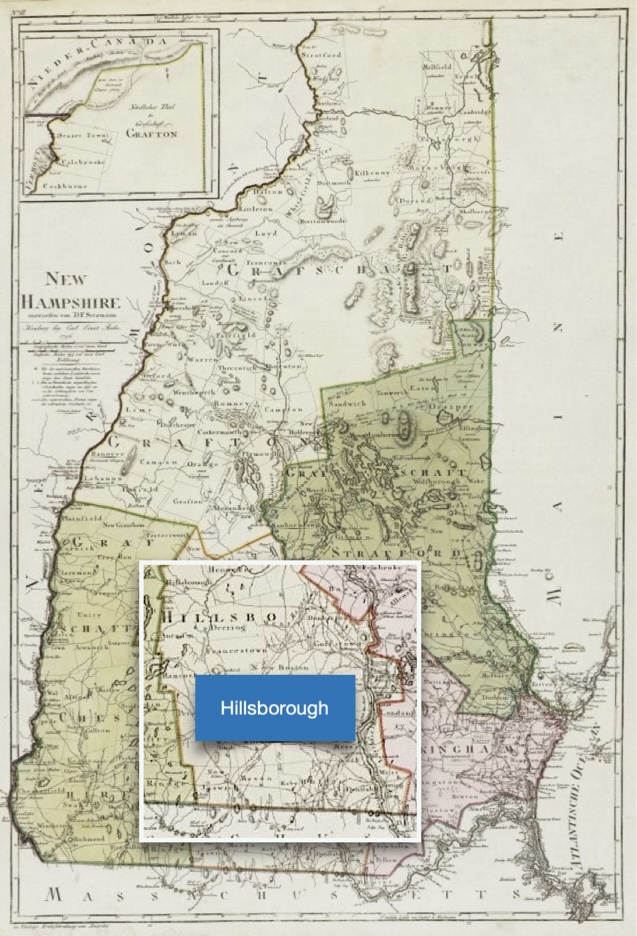
James McClintock, (Sr.), born January 3, 1778 in Hillsborough (town), New Hampshire Province – died September 1845 in Bainbridge, Geauga, Ohio. He married Hephzibah Jones in circa 1803, in New Hampshire. She was born in 1784, in New Hampshire Province – died July 13, 1871 in Laingsburg, Shiawassee, Michigan. They had nine children. The first five were born in Hillsborough (town), Hillsborough, New Hampshire.
- Thirza (McClintock) Taylor, born about 1807 – died June 25, 1893 in Cuyahoga, Ohio.
- Mahala L. (McClintock) Short, born about 1808 – died June 29, 1827 in Phelps, Ontario, New York
- Dr. Freeman Brazilla McClintock, born October 28, 1811 – died March 18, 1882 in Laingsburg, Michigan
- Sarah (McClintock) Short, born about 1812 – died August 10, 1872 in Solon, Cuyahoga, Ohio
- Joshua John McClintock, born about July 29, 1814 – died July 23, 1892 in Solon, Cuyahoga, Ohio
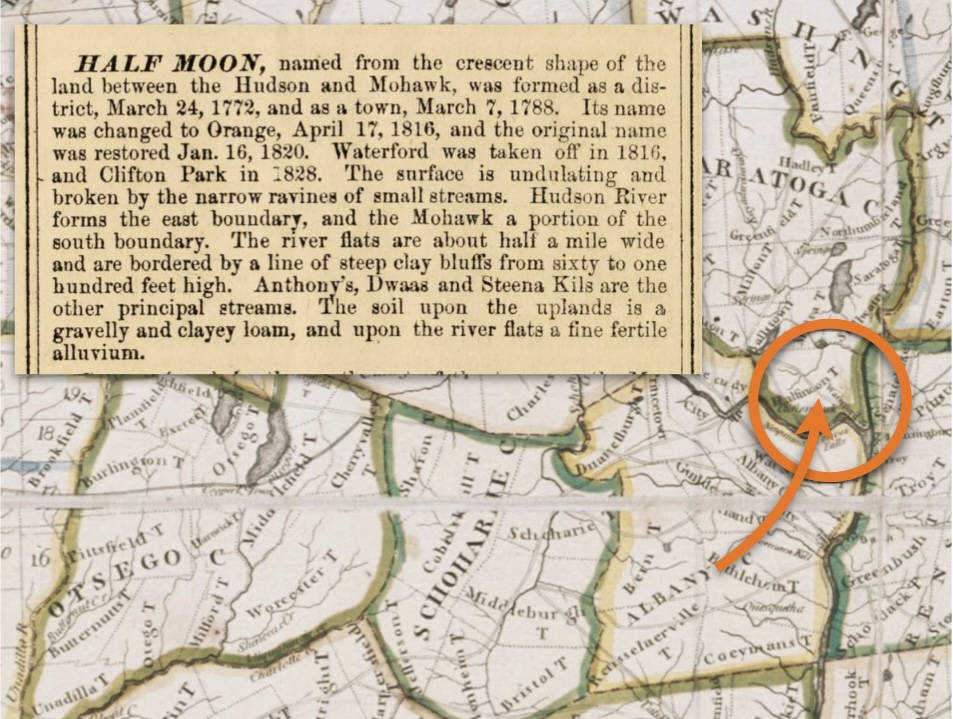
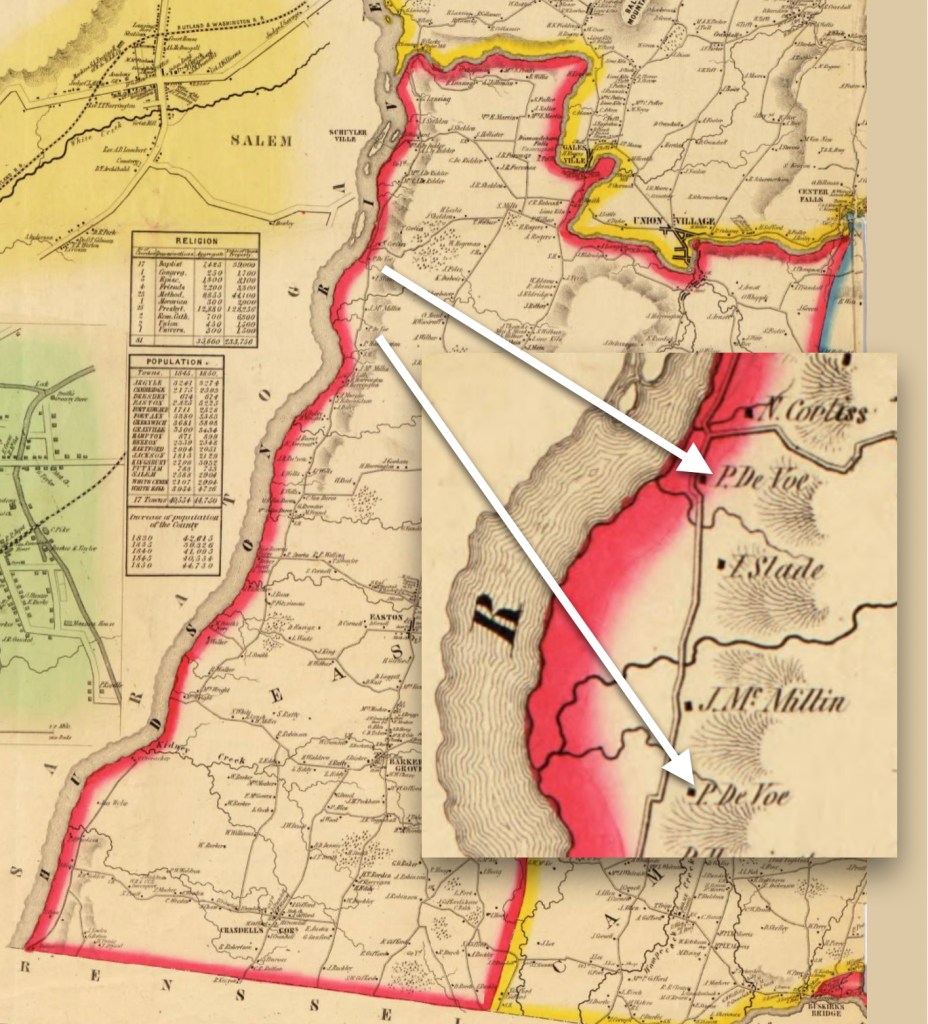
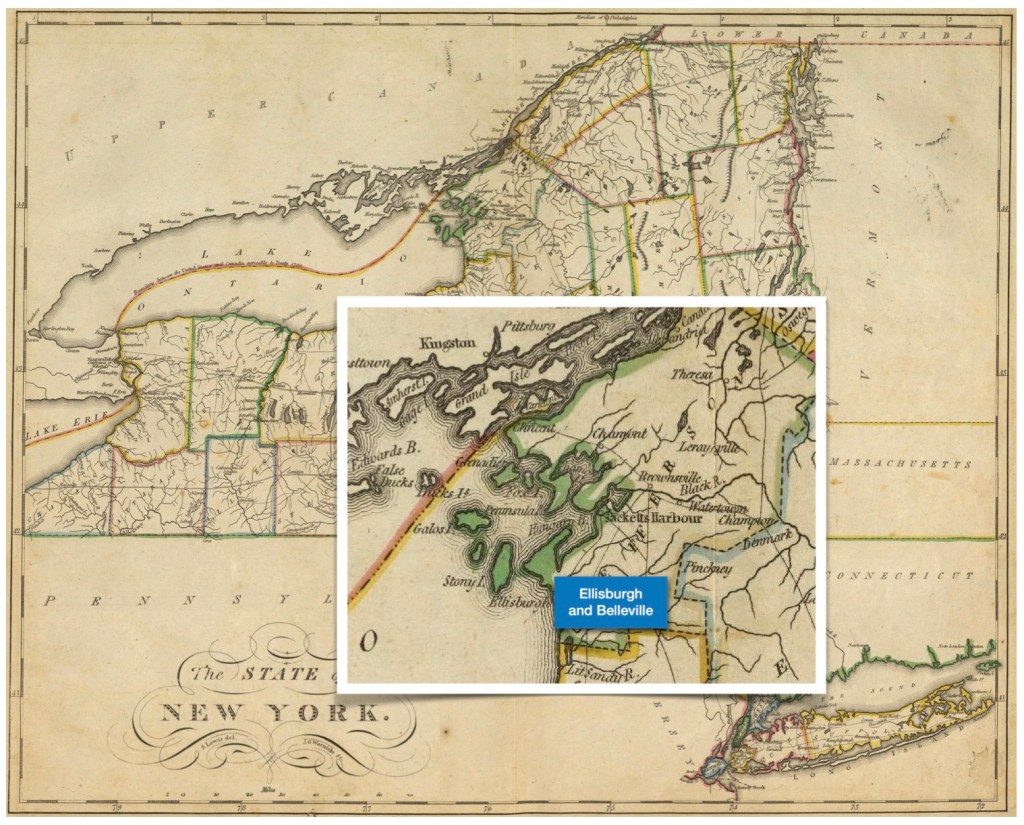
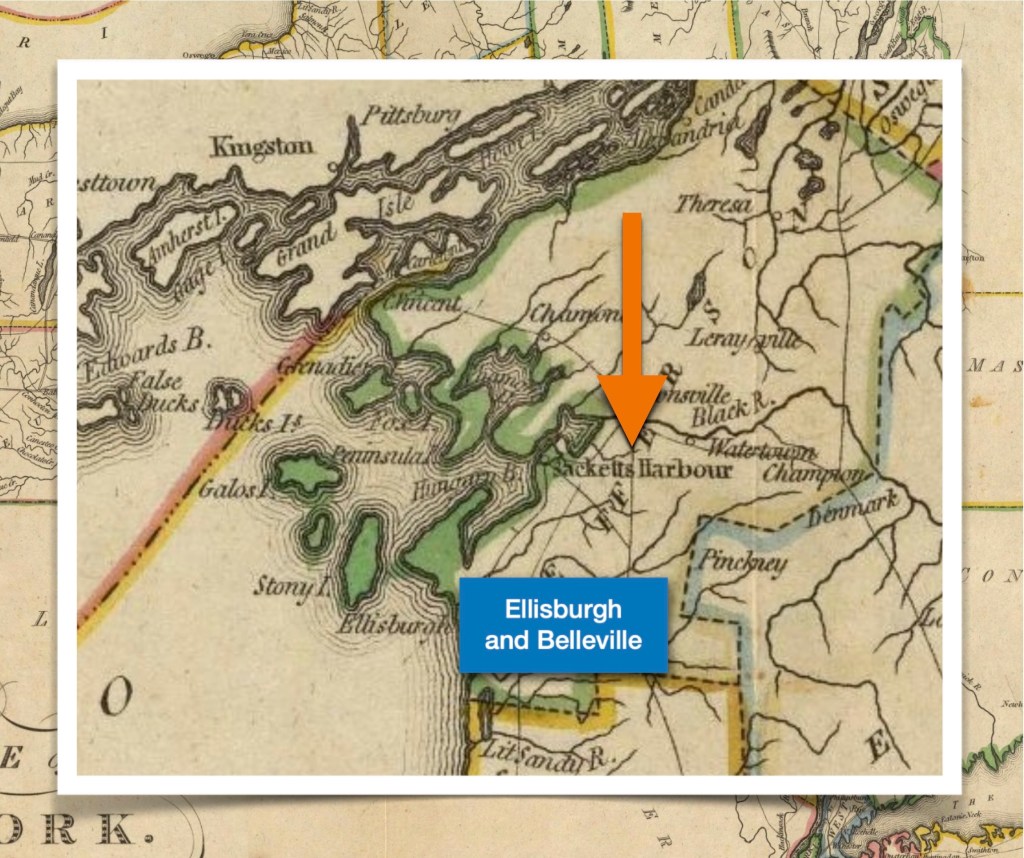
The next four were all born in another county and at the same (new) location, but the location names evolved. Initially the area was Ontario County, New York State, then it became Wayne County, New York in 1823. *Additionally, the town of Arcadia was formed from the Town of Lyons in 1825. - James McClintock (Jr.), born about 1818, Phelps – died January 1, 1854, Bainbridge, Geauga, Ohio
- Dexter McClintock, born August 15, 1819, Phelps – died April 12, 1899, Chagrin Falls, Cuyahoga, Ohio
(We are descended from Dexter.) - William McClintock, born August 13, 1821, Lyons* – died July 6, 1893, West Union, Fayette, Iowa
- Louisa M. McClintock, born about 1827, Arcadia*- died after 1870 location unknown (1)

(Image courtesy of the Library of Congress).
The Censuses of 1800 through 1830 and Their Differences
These censuses are the second, third, fourth, and fifth that the United States had completed. Each year the government was learning a little more about what data it needed to know in able to run the country, and also some new questions to ask. Unfortunately, when we analyze these forms today, we still see many tic marks, but not much detail.
For the 1800 census, James McClintock was unmarried. We do not know with whom he was living in 1800. We are sure in was in Hillsborough, New Hampshire.
The 1810 Census in New Hampshire
Then in 1810, we first encounter the James McClintock family when he and his wife Hephzibah (Jones) McClintock were married and had children living in their home. They were still residing in Hillsborough, New Hampshire where both of them had grown up.


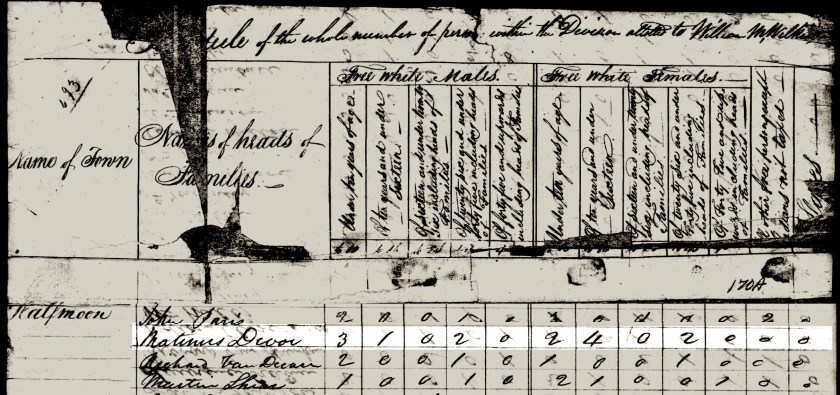
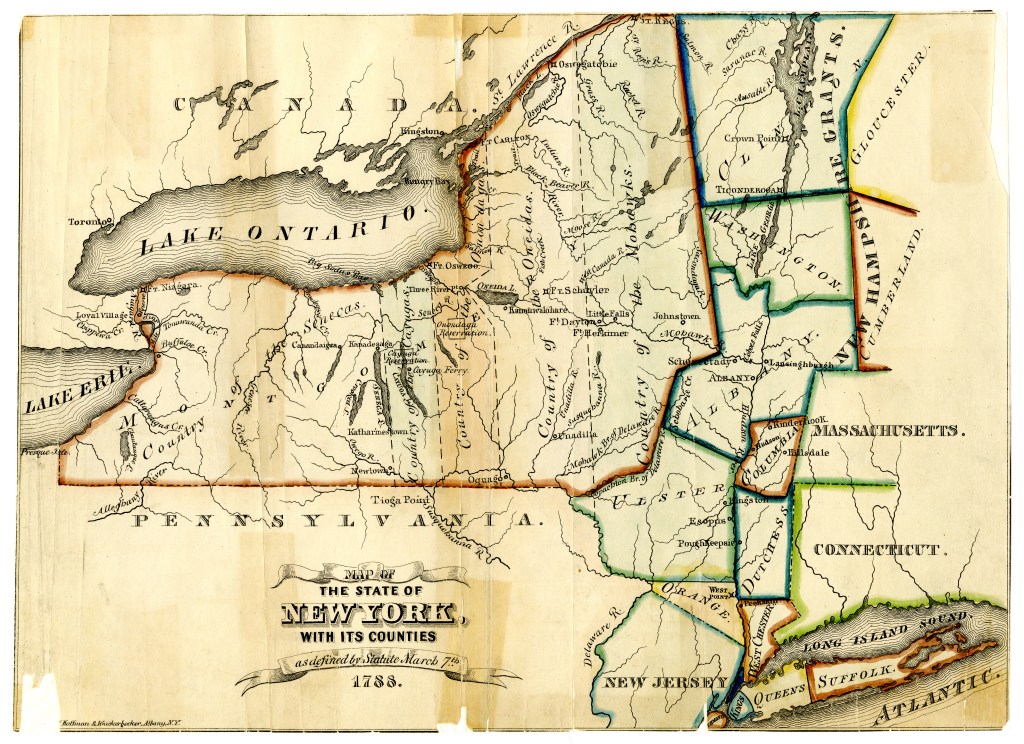
The 1820 Census In New York
By 1820, they have more children and have left New Hampshire behind them. They are now living in the town of Phelps, Ontario County, New York. The reasons that they left New Hampshire are unknown, but there was a large westward migration already occurring in this era. Perhaps they were seeking additional farmland because arable land meant prosperity to farmers. James’s brother Samuel either came with them, or he was already in New York State, which may be one reason why they moved there — there was a family connection.

The 1830 Census In New York
It appears that the family has moved locally from the town of Phelps in Ontario County, to the town of Arcadia, just slightly north in the new (April 1823) Wayne County. This is the first Federal census we see where there is an actual printed form for the census taker to utilize for consistency. Prior to this, many census takers just made up their own forms trying to adhere to guidelines they were given.

From the 1899 obituary that was published for Dexter McClintock in the Chagrin Falls Exponent newspaper, we learned this about his father James McClintock Sr. —
“His father, James McClintock [Sr.], migrated from Massachusetts* to New York, in 1803, where they lived until 1812, when his father struck out to seek his fortune in what was then considered the far west, and after overcoming the many almost insurmountable difficulties, he arrived at what was then called the little pond, now Geauga lake, where he purchased a large tract of land on which to settle with his family, a part of said land, being now owned by Captain C. E. Henry”.
*We believe that this 1899 newspaper account is not correct in several important points, as follows:
- This family is very well documented as living in New Hampshire for several previous generations, since the 1730s. They did not live in Massachusetts.
- The 1810 Census shows them living in New Hampshire, as do the birth records for their children born during this period there.
- The 1820 Census shows them living in New York, as do the birth records for their children born during this period there. Additionally, three siblings were involved through marriages with the local Short family of Phelps, New York.
- It is possible that the father James Sr. could have acquired land in the area, but we do not have records for this. If true, he had done this as an investment, but he was definately not residing in Ohio at that time.
The 1830s
We also know that by this time, that Samuel, [the brother of the father James Sr.] had already left New York state and moved further west to the Ohio Country, where he was paying property taxes as early as 1831 in what is now Solon, Ohio. We believe that it’s plausible that he was the first member of the McClintock branch of our family to arrive there. There was a court case involving Samuel and his brothers which is analyzed in the next chapter, The McClintock Line, A Narrative — Seven, where we explain what was going on.
We also understand that he was quite the drinker… (2)

Let’s Pause A Moment for Some Refreshment, Shall We?
As we learned from the census, for a portion of the 1820s and at the beginning of the 1830s, the James McClintock Sr. family lived in New York State. We came across an interesting account of what it was like to live in Arcadia, New York during this period —
“Up to 1830 the state of temperance was bad enough. Within a distance of three miles along Mud creek there were four distilleries, operated by Harrison, Luce, Sherman, and Mansfield. Whisky was sold as low as twenty-five cents a gallon, and was drank on all occasions. Whether at general training, Fourth of July, logging-bee, raising, or harvesting, the liquor was freely used. It stood upon the sideboard to treat the casual visitor and teacher, doctor, and preacher were alike accustomed to potations from the cup. Ladies met to help along a quilting, and the ‘sling’ imbibed made conversation spirited. If any failed to provide this stimulus it was made a subject of sharp comment. As years went by, a feeling prevailed that this system should be broken up. A preacher found intoxicated was dismissed, and in the county medical society a member accustomed to using liquors to excess was expelled. Still, tippling was common in taverns and in groceries.”
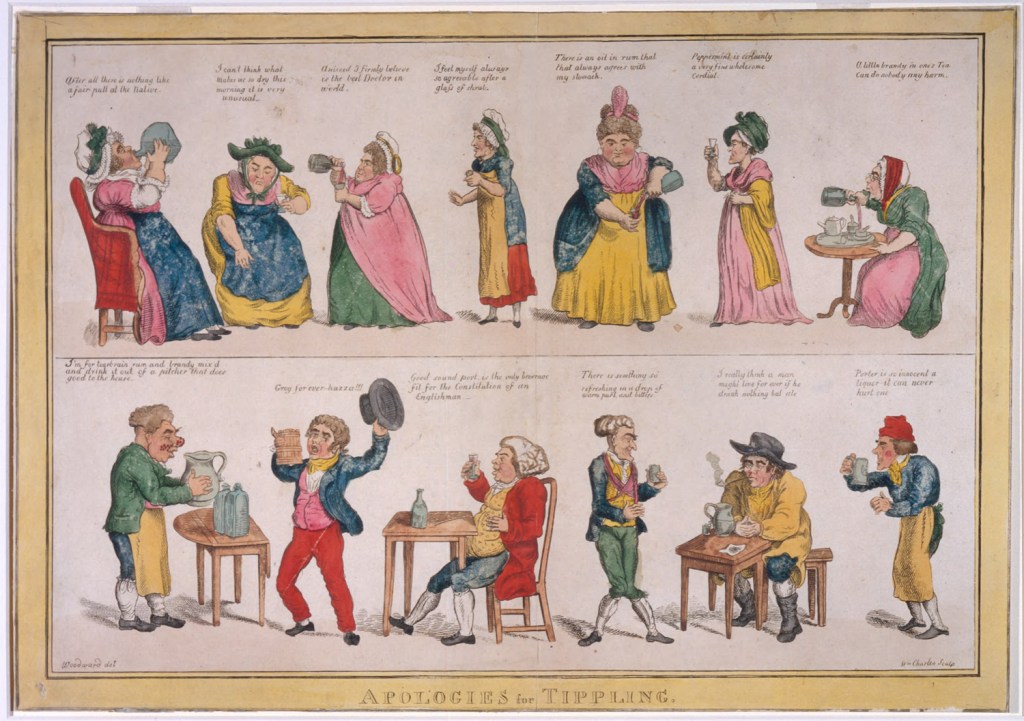

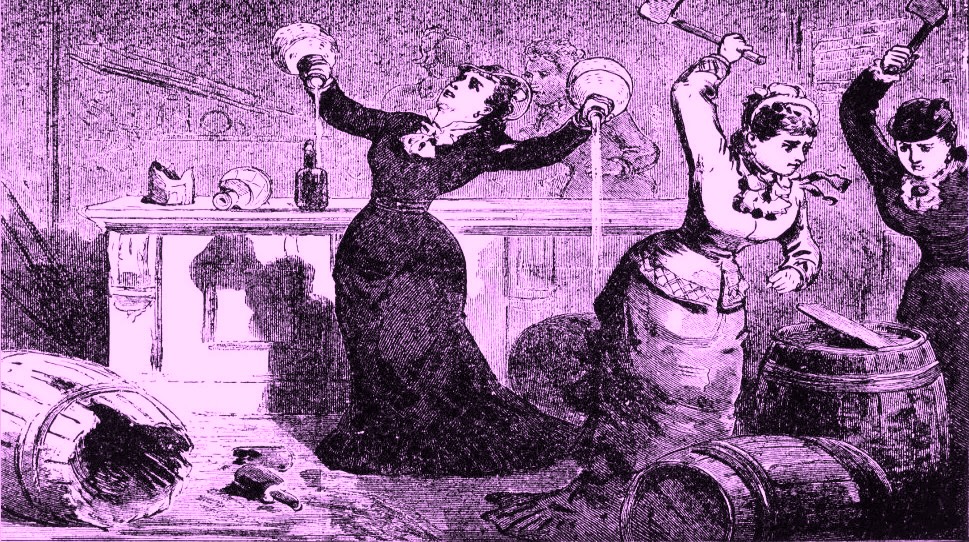
Some of our ancestors were Pilgrims, some were Quakers, some were Presbyterians, some were Catholics — and some were, …non-conformers.
“For the colonists of the 1600s and 1700s much of daily life was filled by tiring drudgery, but throughout the long hours of the work day, beer, cider, rum, and other intoxicating beverages provided a dependable source of comfort. Each day was supplemented by a generous allotment of alcoholic beverages imbibed from their waking hours all the way through the late evening. As author Corin Hirsch states in Forgotten Drinks of Colonial New England, ‘From breakfast cider to afternoon beer to evening flips, toddies and glasses of Canary wine, alcohol lubricated almost every hour of every day’. Drinking accompanied a diverse range of occasions that often took place in taverns, or during meals, work breaks, business meetings, weddings, funerals, trials, and legislative sessions. Daily, day-long ‘tippling’ was simply a fact of life in the colonial period.
While this behavior may be frowned upon in the modern era, colonials viewed the constant intake of liquor as a necessary and beneficial practice. Despite a lack of scientific understanding, the early settlers of North America knew that drinking from certain water sources could make a person deathly ill. Without proper sanitation practices or a way of discerning contaminated water from clean, they largely avoided it, instead seeking hydration from beverages unintentionally sanitized through the processes of fermentation and distillation. Alcohol was not only potable, but also was seen as a healthy, invigorating substance, which was even used in the treatment of disease. While the relatively staid puritan communities of New England such as Windsor admonished drunkenness, they hailed alcohol as the ‘good creature of God’.” (Windsor Historical Society)

Observation: James McClintock Sr.’s 2x Great Grandfather Thomas Mclintoch of Glasgow had been a Maltman (a brewer), and his Grandfather William McClintock was fond of his homemade ‘rhum’…so, it seems like tippling probably ran through the veins of the McClintock family. Despite this, Freeman McClintock maintains in his biographical profile that his “parents instilled into the minds of their children principles of morality and religion”. Perhaps his uncle Samuel never got that family message.
It’s compelling to ponder about how many of our ancestors were likely tipplers, and how over the decades, this behavior paved the way for future temperance movements. (3)
And Back to The Census…
The 1840 Census in Ohio
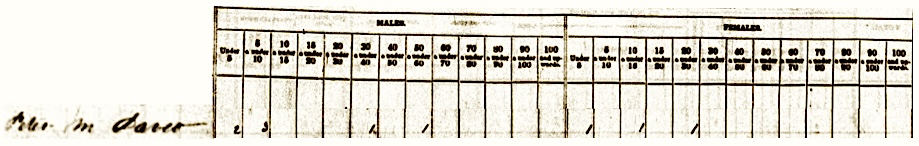
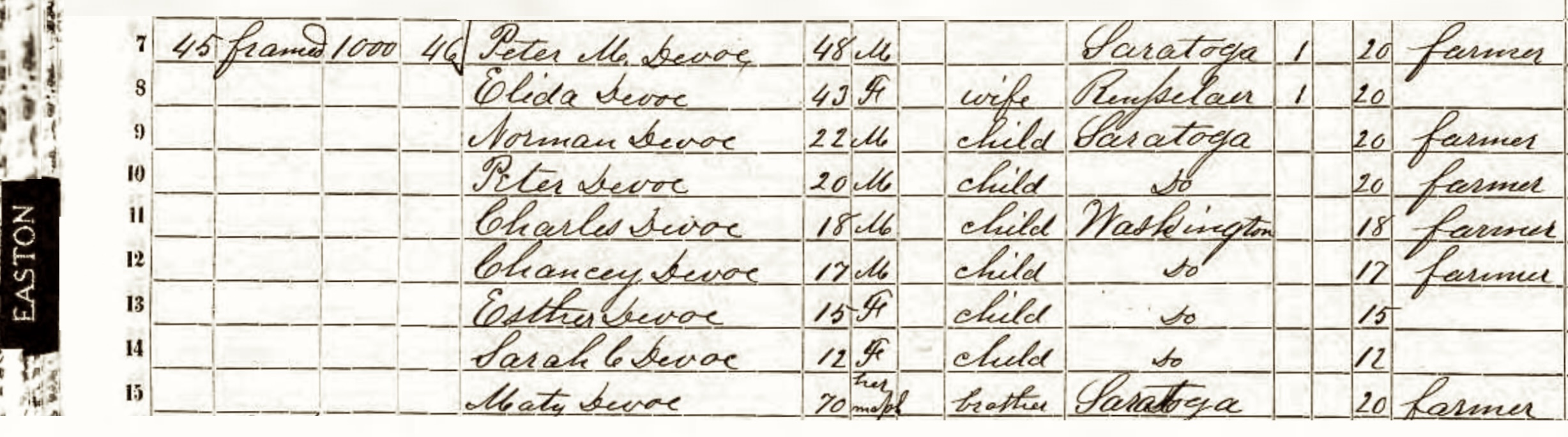
After decades of censuses in other locations, the McClintock family has immigrated in en masse to the Western Reserve of Ohio. We’ve been able to determine through tax records (starting in 1833) that along with James and his wife, most of their adult children also relocated to this area of northeast Ohio.

The census above is for the father James McClintock, Sr. who was living in Bainbridge township at the time of the census. On another 1840 census his son James Jr. and other siblings lived in Solon township. (4)

The Western Reserve of Ohio
In the early part of the 18th century, the Ohio Country was frequently referred to as the West, and from the perspective of New Englanders who settled there, it was indeed pioneer country. By the 1830s and 40s, the Western Reserve wasn’t thought of as a frontier anymore, but actually, it still was in many ways.
The Western Reserve area of northeastern Ohio, was originally established as The Firelands of Ohio, created by the Connecticut legislature in 1792 to help compensate her citizens for their losses when some of the towns were ravaged during the Revolutionary War. Connecticut had a history of belief that her manifest destiny was the inherent right of their northern and southern borders to extend from New England all the way to the Pacific Coast. This area was chartered and land sales were managed by the Connecticut Land Grant Company. The company eventually failed, and Connecticut yielded on their idea of manifest destiny, but the Western Reserve endured. Ohio became a state in 1803.


For all of our many ancestors from here, we believe that this is very true — ”“Following the Revolutionary War, for the next 25 years, Ohio became the primary destination of westward bound pioneers because of the fertile farmland in the Ohio River Valley. Some families stayed for the remainder of their lives.” (Family Search) For the James McClintock Sr. family, when his children were seeking prosperity for their own future families, owning land in Ohio beckoned. (5)

which I did in the Spring of 1980. (Thomas)
The Settling of Solon Township, Ohio
Wikipedia informs us that, “In 1820, the first settlers arrived from Connecticut… The township was named after Lorenzo Solon Bull, who was the son of Isaac Bull, one of the first settlers. Purportedly, the selection of young Lorenzo’s middle name was due to its derivation from the ‘father of democracy’, Solon, the lawmaker of Ancient Greece. The early settlers faced challenges common to pioneers, but in Solon, drainage and wetlands issues complicated settlement and agriculture. Overcoming these obstacles, Solon Township became an arable farming area, producing corn and wheat crops and supporting dairy farms…”
The vast majority of the McClintocks were farmers, with the notable exception of two people, the siblings: Dr. Freeman McClintock, and William McClintock. Although Freeman farmed in Solon, Ohio for a few years, he eventually gave it up and went on to do many remarkable things throughout North America. “The first man who built a house at the Center [of Solon Township] was Freeman McClintock, who located there in 1832 or ’33. He resided there in his log cabin two or three years before any joined him.”

We find this historical anecdote to be interesting, but not completely accurate. We know that his uncle Samuel was already living there. Freeman’s wife Lydia came with him, and his parents arrived in October 1833. Many of his siblings were also leaving New York on the canal boats, schooners, and wagons headed his way. We determined these things based upon his biography and the county tax records. (See footnotes).
William McClintock preferred the legal profession. He was a lawyer, having been admitted to the Ohio Bar in 1849. Eventually he moved his family west to Iowa and became the founder and publisher of a newspaper. (Both brothers have interesting biographical links in the footnotes). (6)
“..Nothing Can be Said to be Certain, Except Death and Taxes…”
We know that the McClintocks had arrived in Ohio by 1831, because there are property tax records in Cuyahoga County which support this. When we analyzed the years 1833 through 1844, we saw some interesting patterns. It appears that in most years, James Sr. either owned most of the land, or was paying most of the taxes for some reason. For example in 1836, James Sr., was paying everyone’s property tax even though some of that land belonged to some of his children. (Gee, thanks dad!)

James Sr. died in September 1845, but the exact date was not recorded.
Later in that same month, there are record documents from a future court case, which state “James Jr., sold the real estate to Dexter McClintock [our ancestor] for $1,125 on September 25, 1845” and that “James Jr. died in 1849[*] and there was considerable dispute among his heirs and the heirs of James Sr., as to the ownership of the property.”
*Correction: James Jr.’s correct death date is recorded as January 1, 1854. He died of typhoid fever, leaving behind a wife and several small children: wife Betsey, and children, Orvil, Antionette, Seth, Edith, and James. (7)
We will be covering this court case in the next chapter, The McClintock Line, A Narrative — Seven). The case caused quite a stir, and involves land, alcoholism, temperance societies, gold, and lots of ruffled feathers.
Following are the footnotes for the Primary Source Materials,
Notes, and Observations
Be Fruitful and Multiply
(1) — thirty two records
Boston Rare Maps
The Sotzmann-Ebeling Map of New Hampshire, Circa 1796
https://bostonraremaps.com/inventory/sotzmann-ebeling-new-hampshire-1796/
Note: For the map image.
James McClintock Sr
in the U.S., Find a Grave Index, 1600s-Current
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/58353478:60525?ssrc=pt&tid=75768616&pid=42330432184
Note: Birth and death dates
and
James McClintock Sr.
https://www.findagrave.com/memorial/95744747/james_mcclintock
and
Ohio Cemetery Records
Gravestone Inscriptions in Old Southwest Burying Ground, Bainbridge, Geauga Co., OH
https://www.ancestry.com/imageviewer/collections/48347/images/OHCemeteryRecords-000382-157?ssrc=&backlabel=Return&pId=304646
Book page: 157, Digital page: 167/506, Lower section, entry 3 from the bottom of the page.
Note: For the data.
Hephzibah ‘Hepsie’ Jones McClintock
https://www.findagrave.com/memorial/92303259/mccl
Note: For the data. There are some minimal family records.
Hepzidah McClintock
in the Michigan, U.S., Death Records, 1867-1952
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/1403875:60872?tid=&pid=&queryId=78c1cb54-4fc6-46dd-897e-ede148c8d4b1&_phsrc=orQ32&_phstart=successSource
Book page: 203, Digital page: 590/651, Left page, entry 636.
Notes: The information for her parents, and the county name, are incorrect on this file (transcription errors?). She appears to have been living with her son Dr. Freeman McClintock, who died in Michigan.
Thirza Taylor
in the Ohio, U.S., Wills and Probate Records, 1786-1998
Cuyahoga > Estate Files, Docket 34, Case No 9031-62092, 1813-1913
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/6426020:8801
Digital pages: 2 through 7/209
and
The Connection: When Thirza’s younger brother James Jr. died on January 1, 1854, his wife Betsey McClintock remarried eight months later (on August 10, 1854), to Tirza’s son Philonzo Taylor Jr. (Thirza lost a brother and gained a daughter-in-law). Here is the 1850 census to document the Taylor family —
Thirza Taylor
in the 1850 United States Federal Census
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/13469152:8054?tid=&pid=&queryId=0d8c99c5-6e9b-49d3-af1f-1446805483c0&_phsrc=IPg31&_phstart=successSource
Digital pages: 9-10/30, Entries 38-42, and 1-4 (next page top).
and
The August 10, 1854 remarriage:
Betsey Ann McClintock
in the Ohio, U.S., County Marriage Records, 1774-1993
Geauga > 1841 – 1854
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/900862477:61378?tid=&pid=&queryId=7b4f7af5-2a9c-4c25-a297-4327d843e3c4&_phsrc=IPg6&_phstart=successSource
Digital page: 412/437, Left page, entry 2.
Mahala Short
in the U.S., Find a Grave Index, 1600s-Current
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/26447561:60525?tid=&pid=&queryId=ce7d9371-67a5-4f32-b666-460c32adfea5&_phsrc=Lml7&_phstart=successSource
and
Mahala Short
https://www.findagrave.com/memorial/53699209/mahala-short
Notes: We connected her husband Shubal Short through her residence with her family who lived in Phelps, Ontario, New York and this lawsuit, where her husband is named: https://www.ancestry.com/imageviewer/collections/28306/images/dvm_LocHist012267-00246-1-0?ssrc=&backlabel=Return&pId=400
Notes: The McClintock family is connected to the Short family of Phelps, Ontario County, New York through 3 marriages:
- Sarah McClintock, married Sidney Smith Short about 1831
- Mahala McClintock, married Shobal Short Sr. about 1826
- Freeman Brazilla McClintock, Lydia A. Short, on November 27, 1831, as identified in American Biographical History of Eminent and Self-made Men : Michigan volume, The Sixth Congressional District
Sarah Short
in the U.S., Find a Grave Index, 1600s-Current
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/240596827:60525?tid=&pid=&queryid=b36b7940-22da-4780-81b1-d3898638aab9&_phsrc=TNP3&_phstart=successSource
and
Sarah McClintock Short
https://www.findagrave.com/memorial/269813108/sarah-short
Notes: The McClintock family is connected to the Short family of Phelps, Ontario County, New York through 3 marriages: - Sarah McClintock, married Sidney Smith Short about 1831
- Mahala McClintock, married Shobal (Shubael) Pula Short Sr. about 1826
- Freeman Brazilla McClintock, married Lydia A. Short, on November 27, 1831, as identified in American Biographical History of Eminent and Self-made Men : Michigan volume, The Sixth Congressional District
Dr Freeman McClintock
in the U.S., Find a Grave Index, 1600s-Current
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/86876122:60525?tid=&pid=&queryId=2b92d9cc-fbdc-4124-862f-bcb7bc69167a&_phsrc=aWz3&_phstart=successSource
and
Dr Freeman McClintock
https://www.findagrave.com/memorial/33127439/freeman-mcclintock
Note 1: For the data on birth and death dates.
Note 2: The McClintock family is connected to the Short family of Phelps, Ontario County, New York through 3 marriages:
- Sarah McClintock, married Sidney Smith Short about 1831
- Mahala McClintock, married Shobal Pula Short Sr. about 1826
- Freeman Brazilla McClintock, Lydia A. Short, on November 27, 1831, as identified in American Biographical History of Eminent and Self-made Men : Michigan volume, The Sixth Congressional District

Dr. Freeman McClintock led a dynamic life and was profiled in this book — American Biographical History of Eminent and Self-made Men: Michigan volume, The Sixth Congressional District
https://www.ancestry.com/imageviewer/collections/25026/images/dvm_LocHist010122-00622-0?pId=704
Book pages: 50-51, Digital pages: 797-798/984
Note: For the text.
image4
Handwritten note, Ancestry gallery image for Joshua John McClintock
https://www.ancestry.com/mediaui-viewer/collection/1030/tree/1173647/person/-1913123119/media/11ee9170-8904-4927-9240-ed38c9b3fa82?queryId=8f38b5df-7553-47d9-b0ec-1f41dd4ae931&_phsrc=xAm11&_phstart=successSource
Notes: Below is the handwritten document, that also provides information about his wife Lucy Seward. His birth location is incorrect being listed as Manchester. The family never lived in Manchester, but in the nearby town of Hillsborough, where his other siblings from the same timeframe were likely born.

J J McClintock
in the Ohio, U.S., Wills and Probate Records, 1786-1998
Cuyahoga > Will Records, Vol X-Y, 1892-1893
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/13657472:8801?tid=&pid=&queryId=1dbe9c61-e191-4563-aedd-fb10ce11e962&_phsrc=AKd1&_phstart=successSource
Digital page: 206/682
Note: For death date.
and
will [of JJ McClintock]
https://www.ancestry.com/mediaui-viewer/collection/1030/tree/1173647/person/-1913123119/media/7a207c15-7b42-4acf-b42b-b3fc2648f551?galleryindex=1&sort=-created
and
will p2
https://www.ancestry.com/mediaui-viewer/collection/1030/tree/1173647/person/-1913123119/media/54bd5581-d1fe-4174-90d8-1993a9606f73?galleryindex=2&sort=-created
Note: There are two pages to this hand drafted document as indicated by the two links above. The Will is found in an ancestry.com photo gallery.
James McClintock [Jr.]
https://www.findagrave.com/memorial/53699189/james_mcclintock
Note: For his birth and death dates.
Dexter McClintock
in the Web: Ohio, Find A Grave Index, 1787-2012
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/7887384:70559?ssrc=pt&tid=18269704&pid=635845738
and
Dexter McClintock
https://www.findagrave.com/memorial/19154853/mccl
Note: For the data.

William McClintock
https://www.findagrave.com/memorial/108474075/william_mcclintock
Notes: For his birth and death dates.
Observation: Not to be outdone by his older brother Freeman, it appears that William McClintock was also a very accomplished man. A newspaper he started named the Fayette County Union was published continuously until 1944.
Portrait and Biographical Album of Fayette County, Iowa.
Containing Full Page Portraits and Biographical Sketches of Prominent and Representative Citizens of the County
by Lake City Publishing Company
https://archive.org/details/portraitbiogra00lake/page/272/mode/2up?view=theater
Book page: 273, Digital page: 272/698
and a transcribed copy —
Fayette County, Iowa
Biography Directory
Portrait & Biographical Album of Fayette County Iowa
Containing Full Page Portraits and Biographical Sketches of Prominent and Representative Citizens of the County
Lake City Publishing Co., Chicago, March 1891
https://iagenweb.org/fayette/bios/1891/373b.htm
Library of Congress
Fayette County Union (West Union, Iowa) 1866-1944
https://www.loc.gov/item/sn83025183/
Note: For the data.
Louisa McClintock
in the 1870 United States Federal Census
Michigan > Shiawassee > Sciota
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/27514564:7163?tid=&pid=&queryid=2efdaa07-be2b-4470-a5cc-681975d47192&_phsrc=dPv25&_phstart=successSource
Book page: 2, Digital page: 2/32, Entries 12 and 13.
Notes: For the data. Louisa’s birthdate is inferred from this record. In 1870, she is living in Michigan taking care of her mother, who died there the next year.
The Connection: Throughout the 1850s and 186os she is making property tax payments in Solon, Cuyahoga, Ohio. The last record for Ohio is:
Louisa M McClintock
in the Cuyahoga County, Ohio, U.S., Tax Lists, 1819-1869
1865
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/1320613:2100?tid=&pid=&queryid=8220d991-1796-464a-8766-f71723b626c5&_phsrc=FPj1&_phstart=successSource
Book page: 26, Digital page: 500/558
Note: For the data.
Wayne County, New York
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wayne_County,_New_York
Note: For founding date.
Library of Congress
A View of Manchester, N.H.
by J.B. Bachelder, 1855
https://www.loc.gov/resource/cph.3g08323/
Note: For the landscape painting.
The Censuses of 1800 through 1830 and Their Differences
(2) — twelve records
The National Archives
The 1810 Census
https://www.archives.gov/research/census/1810
Note: “The census began on Monday, August 6, 1810, and was finished within 9 months…” and for the form questions:
https://www.archives.gov/files/research/genealogy/charts-forms/1810-census.pdf
James McClintock
in the 1810 United States Federal Census
New Hampshire > Hillsborough > Windsor
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/187893:7613?ssrc=pt&tid=18269704&pid=635866414
Digital page: 2/2, Entry 16.
Note: For the data.
Map Of The State Of New York
Published by A. Finley Philadelphia,1824
https://archive.org/details/dr_map-of-the-state-of-new-york-published-by-a-finley-philada-1824-copy-ri-2587002
Note: For the map image.
The National Archives
1820 Census Records
https://www.archives.gov/research/census/1820
Note: “The census began on Monday, August 7, 1820, and was finished within 6 months…” and for the form questions:
https://www.archives.gov/files/research/genealogy/charts-forms/1820-census.pdf
Note: For the data.
James McClintock
in the 1820 United States Federal Census
New York > Ontario > Phelps
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/567539:7734?ssrc=pt&tid=18269704&pid=635866414
Digital page: 10/12, Entry 11.
Note: He is entry #738 and the next entry #739, is his brother Samuel.
D. McClintock 1899 obituary
Chagrin Falls Exponent newspaper
https://www.ancestry.com/mediaui-viewer/collection/1030/tree/198643829/person/292609290256/media/e1a020c0-adb6-4ce0-8bf8-3a1d4785e51e?galleryindex=3&sort=-created
Note: April 20, 1899 issue, page 5.
The National Archives
1830 Census Records
https://www.archives.gov/research/census/1830
Note: “The census began on Tuesday, June 1, 1830, and was finished within 6 months,…” and for the form questions:
https://www.archives.gov/files/research/genealogy/charts-forms/1830-census.pdf
Note: For the data.
James McClintick
in the 1830 United States Federal Census
New York > Wayne > Arcadia
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/163551:8058
Digital page: 35/48, Entry 17.
Note: For the data.
Samuel McClintock
in the Cuyahoga County, Ohio, U.S., Tax Lists, 1819-1869
1831-1833
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/1665566:2100?tid=&pid=&queryid=c0b09afb-af21-4cc1-ae13-d957d6a769a8&_phsrc=NeN1&_phstart=successSource
Digital page: 194/636, Last entry.
Note: For the data.
Let’s Pause A Moment for Some Refreshment, Shall We?
(3) — three records
History of the Town of Arcadia
https://wayne.nygenweb.net/everts/arcadiaeverts.html
Note: For the data.
Windsor Historical Society
Colonial Boozing
https://windsorhistoricalsociety.org/colonial-boozing/
Note: For the text.
Medium
The Temperance Movement Was Totally Badass
https://medium.com/@benfreeland/the-temperance-movement-was-truly-badass-dfeaed03a3e0
Note: For temperance illustration of Fredericktown, Ohio reformers.
You go, girls!
And Back to The Census…
(4) — three records
The National Archives
1840 Census Records
https://www.archives.gov/research/census/1840
Note: “The census began on Monday, June 1, 1840, and was finished within five months…” and for the form questions:
https://www.archives.gov/files/research/genealogy/charts-forms/1840-census.pdf
Note: For the data.
James Mcclintock
in the 1840 United States Federal Census
Ohio > Geauga > Bainbridge
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/2629792:8057?ssrc=pt&tid=18269704&pid=635866414
Digital page: 9/14, Entry 3.
Note: For the data.
The Western Reserve of Ohio
(5) — four records
Western Reserve Including the Fire Lands 1826
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Western_Reserve_Including_the_Fire_Lands_1826.jpg
Note: On this map, Geauga County is still combined with the future Lake County and Russell township is not yet named.
Note: For the map image.
History of the Firelands
https://lymevillage.org/history-of-the-firelands/
Note: For the text.
United States Migration to Ohio, Northwest Territory, Southwest 1785 to 1840 – International Institute
https://www.familysearch.org/en/wiki/United_States_Migration_to_Ohio,Northwest_Territory,_Southwest_1785_to_1840-_International_Institute
Note: For the text.
Connecticut Western Reserve
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Connecticut_Western_Reserve
Note: For the map of “Connecticut’s land claims in the Western United States.”
The Settling of Solon Township, Ohio
(6) — three records
Solon, Ohio
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solon,_Ohio
Note: For the text.
Granger Art on Demand
Ohio Log Cabin and Farm
by Artist unknown
https://grangerartondemand.com/featured/ohio-log-cabin-farm-granger.html
Note: For the cabin image.

History of Cuyahoga County, Ohio …
With Portraits and Biographical Sketches of its Prominent Men and Pioneers
by Crisfeld Johnson
https://archive.org/details/historyofcuyahog00injohn/page/516/mode/2up?q=“McClintock”
Book page: 517, Digital page: 516/534
Note: For the data.
“Nothing Can be Said to be Certain, Except Death and Taxes…”
(7) — seven records
Death and Taxes [idiom]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Death_and_taxes_(idiom)#:~:text=%22Death%20and%20taxes%22%20is%20a,certain%2C%20except%20death%20and%20taxes.
Note: For the data.
James Mcclintock
in the Cuyahoga County, Ohio, U.S., Tax Lists, 1819-1869
1833-1835
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/1651638:2100?ssrc=pt&tid=18269704&pid=635866414
Digital page: 65/658, Entries 8 through 17 (based upon name).
Note: For the data.
James McClintock
in the Cuyahoga County, Ohio, U.S., Tax Lists, 1819-1869
1835-1837
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/1647946:2100?ssrc=pt&tid=18269704&pid=635866414
Digital page: 487/648, Entries 7 through 18 (based upon name).
Note: For the data.
James McClintock
in the Cuyahoga County, Ohio, U.S., Tax Lists, 1819-1869
1842-1843
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/1607066:2100?ssrc=pt&tid=18269704&pid=635866414
Digital page: 537/686, Entries 10 through 14 (based upon name).
Note: For the data.
James McClintock
in the Cuyahoga County, Ohio, U.S., Tax Lists, 1819-1869
1844-1845
https://www.ancestry.com/discoveryui-content/view/1195813:2100?ssrc=pt&tid=18269704&pid=635866414
Digital page: 303/682, Entries 12 through 17 (based upon name).
Note: For the data.
Listed in the Cuyahoga County 1852 landownership map index
https://www.ancestry.com/imageviewer/collections/21248/images/dvm_LocHist007250-00029-1?ssrc=pt&treeid=18269704&personid=635866414&usePUB=true&pId=52
Digital page: 54/107, Entry 20.
Note: For the data.
Annals of Cleveland.
Vol. II. Abstracts of the records of court cases in Cuyahoga County
https://www.ancestry.com/imageviewer/collections/28306/images/dvm_LocHist012267-00246-1-0?ssrc=&backlabel=Return&pId=400
Book page: 111-112, Digital page:: 470-471/3048
Note: For the data.